In 1984, The New York Times published an article imagining a distant future in manufacturing, where production lines were so automated they could run 24/7 without even needing light. Fast-forward to 2025, and that future has arrived. Factories like Xiaomi’s fully automated facilities are already operating at scale.
Early visions of automation focused almost entirely on the production process. Areas like safety procedures or regulatory compliance were rarely part of the picture. Today, however, integrating AI into those domains is often a low-hanging fruit – offering significant gains without major costs, especially with the rise of generative artificial intelligence.
Thanks to its repetitive workflows and tightly controlled environments, the manufacturing sector is a natural fit for AI-driven regulatory compliance powered by machine learning. In this article, we unpack how AI supports compliance in manufacturing, explore real-life examples, and highlight how different roles on the factory floor are affected by compliance risks.
Why AI risk management and compliance can provide you with competitive advantage in manufacturing?
In the manufacturing industry, regulatory requirements are more likely to increase than decrease. As globalization intensifies and international trade expands, manufacturers are faced with growing regulatory responsibilities.
Regional organizations of states such as the European Union (EU), African Union (AU), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA) facilitate the exchange of goods and boost profits. However, they also enforce shared legal frameworks that manufacturers must comply with. This adds another layer of legal expectations on top of national laws, increasing the burden on companies that must simultaneously meet regional and domestic standards.
In recent years, new challenges have emerged, driven by goals to reduce CO2 emissions, stricter worker and process safety expectations, and disruptions caused by global pandemics, supply chain crises, and geopolitical conflicts. These have significantly increased compliance complexity.
AI-driven compliance for manufacturing, as we will demonstrate below, allows companies to navigate these challenges without significantly increasing costs – and in many cases, helps avoid multi-million-dollar penalties.
Compliance in manufacturing: Law, safety, quality, sustainability
What does compliance mean in a manufacturing context? Unlike many other industries, the scope of compliance-related responsibilities is exceptionally broad. Requirements pile up from every direction –government agencies, supranational bodies, business partners, certification bodies, and consumers.

How AI transforms compliance and risk management
Regulatory compliance in manufacturing spans multiple domains, and frequent changes in legal frameworks only complicate the picture further. When a product meets US requirements for composition, packaging, or sustainability, it might still fail in the EU. For example, ractopamine (a pork growth promoter) is banned in the EU under Commission Regulation (EC) No 470/2009, yet still permitted in the US by the FDA .
Combine that with fragmented data from ERP, MES, LIMS, paper records, and manual workflows, and you have a recipe for errors, delays, and compliance gaps. And the stakes are enormous: manufacturers who cut corners may face fines, recalls, lawsuits, and severe damage to human safety and brand reputation – like when Blue Bell Creameries lost trust and market share following a deadly listeria outbreak tied to compliance failures.
Legal compliance
Legal compliance involves adhering to all applicable laws, regulations, and contractual obligations at the local, national, and international levels.
Regulatory authorities:
- European Union: European Medicines Agency (EMA), European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), and specific sectoral regulations like the MDR (Medical Device Regulation).
- United States: Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA).
- Asia-Pacific: Varies widely; for instance, Japan’s PMDA for pharmaceuticals, China’s NMPA for medical devices, or Singapore’s NEA for environmental rules.
- Africa and LATAM: Often rely on hybrid regulatory models based on EU/US frameworks but with additional import/export compliance requirements.
Key requirements:
Legal compliance touches virtually every aspect of operations – from product approvals, employee rights, intellectual property, to export controls.
- Pharma and medical devices: require documentation of every stage of production, batch tracking, and regulatory submissions.
- Chemical and heavy industry: face stringent requirements under REACH (EU) or TSCA (US).
Challenges:
- Constant regulatory changes
- Overwhelming documentation
- Jurisdictional misalignment
How AI helps:
AI-powered regulatory intelligence platforms can track and parse new laws and guidelines across jurisdictions in real-time, using natural language processing (NLP) to flag only the relevant updates by industry or geography.
Machine learning (ML) models can automate document generation and classification, ensuring submissions (e.g. to EMA or FDA) follow correct formats.
AI agents in manufacturing can also cross-map definitions (e.g., safety or risk) between US, EU, or Asia to surface conflicts and automate reconciliation efforts, significantly reducing legal ambiguity and manual legal review work.
Safety compliance
Safety compliance ensures that workplaces, products, and processes do not pose unacceptable risks to employees, consumers, or the environment.
Regulatory authorities:
- Global: International Labor Organization (ILO), ISO 45001 standards.
- US: OSHA enforces workplace safety.
- EU: Directives on worker protection (Directive 89/391/EEC), and national labor inspections.
- Asia: Singapore’s Workplace Safety and Health Act, China’s Work Safety Law.
Key requirements:
- Workplace safety protocols: protective gear, equipment maintenance, training, emergency procedures.
- Product safety: Failure modes and effects analysis (FMEA), material safety, proper labeling.
- Incident logging and reporting.
Challenges:
- Real-time hazard monitoring
- SOP adherence
- Expensive inspections
How AI helps:
Computer vision systems powered by AI can monitor video feeds for unsafe behavior (e.g., missing PPE or incorrect equipment use) and alert supervisors instantly.
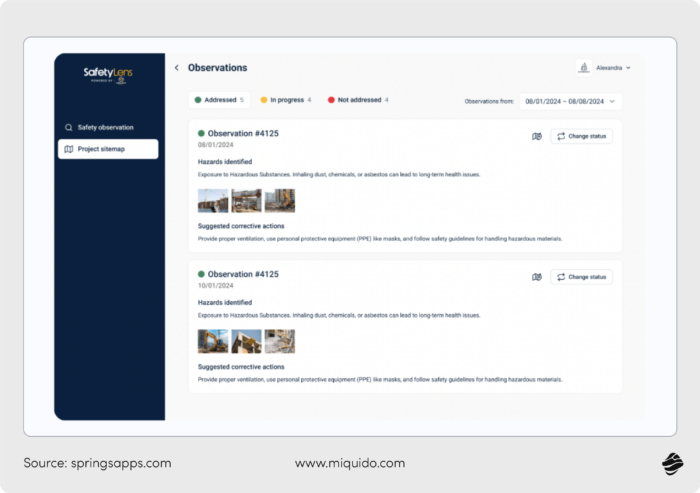
AI chatbots can serve as digital safety assistants, reminding workers of protocols contextually and even conducting pre-shift check-ins.
Predictive analytics can forecast equipment failure risks or workplace accidents by analyzing maintenance logs, IoT sensor data, and historical incidents – cutting down on both costs and downtime from manual inspections.
Quality compliance
Quality compliance ensures that products meet required standards and are consistently produced according to specifications.
Regulatory authorities:
- US: FDA’s Current Good Manufacturing Practice (CGMP).
- EU: ISO 9001, MDR quality requirements.
- Food industry: Global Food Safety Initiative (GFSI), HACCP, BRCGS standards.
Key requirements:
- Documented quality management systems.
- Non-conformance tracking, corrective/preventive action (CAPA).
- Validation and verification of processes and equipment.

Challenges:
- Small deviations triggering recalls
- Dispersed quality data
- Audit readiness
How AI helps:
AI-enabled sensors and anomaly detection models can catch subtle deviations in production data (e.g., temperature, pressure, viscosity) before they lead to non-compliance. These models improve over time with more data, becoming better at identifying quality risks early.
Natural language generation (NLG) tools can auto-generate CAPA reports and summarize quality incidents for audits, while centralized AI platforms unify quality metrics from multiple facilities or vendors, ensuring compliance with ISO or FDA standards at scale.
Environmental compliance
Environmental compliance ensures that manufacturing processes minimize harm to the environment and meet sustainability goals and legal thresholds.
Regulatory authorities:
- EU: European Environment Agency (EEA), REACH, Emissions Trading Scheme.
- US: EPA, Clean Air and Clean Water Acts.
- Asia: National laws with growing regional coordination (e.g., ASEAN Agreement on Transboundary Haze Pollution).
Key requirements:
- Emission monitoring and reporting (CO₂, NOx, SOx, VOCs).
- Safe waste handling and disposal.
- Sustainable sourcing, recycling obligations, environmental impact assessments.
Challenges:
- Emissions tracking
- Leak detection
- Fast-changing standards
How AI helps:
AI-integrated IoT systems can continuously monitor emissions (CO₂, NOx, VOCs) and compare them against dynamic regulatory thresholds, sending real-time alerts when nearing limits.
Additionally, AI can automate ESG reporting, generating Scope 1, 2, and even Scope 3 disclosures by analyzing energy use, transport data, and supplier metrics, keeping companies ahead of evolving sustainability regulations.
Sector spotlight: Heavily regulated industries & the potential of AI in manufacturing compliance
Manufacturing compliance is a tough nut to crack, but some niches raise the bar exceptionally high. Let’s take a look at a few of them and real-life cases that show how AI can play a crucial role in preventing compliance issues, carrying out sophisticated data analytics and supporting human expertise.
Pharmaceuticals & medical devices
Compliance challenges lurk around every corner for pharmaceutical and medical device manufacturers. Strict relevant regulations apply not only to the product itself – its composition, testing, dosage, format –also to packaging, market entry, and distribution.
Maintaining compliance across global markets is another major challenge. Regulatory requirements vary greatly across regions, making this one of the most complex sectors, alongside food and beverage.
For instance, in 2021, the continuous glucose monitoring system from Senseonics received relatively fast FDA approval but is facing delays in the EU due to EMA's demand for longer-term data.
The medical compliance institutions are not afraid of harsh fines: a stark example is the Sanofi-Aventis US case, where the company was fined $190 million for inflating the price of a drug for radiation patients. In another case, GlaxoSmithKline paid a record $3 billion settlement over allegations of misbranding and failing to report safety data.
AI use case in pharma compliance: Harmonizing global documentation (multilingual AI)
Before launching any drug, it must go through a series of clinical trials. But beyond testing, the results must be submitted to regulatory bodies across different markets – and often in several languages.
What happens when deadlines are tight, and those documents arrive in French, Japanese, or German, each containing key sensitive data needed for regulatory approval? According to this case study from v500, one pharma giant faced this very challenge, and used generative AI to overcome it.
Human translators estimated a two-month turnaround, but working under pressure could have led to costly mistakes. The AI solution processed more than 2,000 pages of clinical documentation across three languages. It automatically extracted key safety and efficacy data, flagged translation inconsistencies, and generated English summaries ready for submission.
The result: $800,000 saved on expedited translation costs and $11 million in potential market loss avoided thanks to on-time launch.
GRAPHIC: Pangea AI – mamy
And this isn’t the only scenario where AI can help pharma companies avoid regulatory delays, launch postponements, and reputational damage among investors.
Other high-impact GenAI use cases in pharma compliance include:
- Early detection of post-market adverse event patterns across global submissions
- Mapping anomalies across trial formats and cross-referencing against regulatory rules
- Auto-generating multilingual submissions for simultaneous global filing
Food manufacturing & food tech
Food and beverage is another industry under tight scrutiny and strict regulation. Requirements differ significantly by country, region, or trade bloc – and enforcement practices vary widely between authorities.
For example:
- Titanium dioxide is banned as a food additive in the EU (since 2022) but still permitted in the US.
- California’s Prop 65 demands lead labeling in spices, while other US states and the EU don’t enforce such rules.
- A seasoning mix legal in Canada was rejected in Brazil due to stricter ANVISA thresholds on undeclared allergens.
AI use case in food manufacturing compliance: Multi-level alignment with regulation updates
Consider lawsuits under California’s Prop 65 filed against spice and rice manufacturers. These cases were dismissed in March and November 2023 after courts accepted a new NHANES-based testing methodology.
This regulatory change is substantial, and AI can facilitate seamless adaptation. It supports contamination detection, supply chain traceability, allergen alerts, and batch-level anomaly detection using analyzing vast amounts of data.
For instance:
- AI systems can flag specific spice batches for potential lead contamination based on origin and sourcing
- Computer vision can detect adulterants like lead chromate in real-time using high-res imaging
- Real-time alerts can be issued in accordance with new NHANES-aligned testing standards
Other recent regulatory changes include:
- FDA's 2023 guidance on gluten-free labeling requirements
- EU’s 2022 ban on titanium dioxide as a food additive
These updates often require recalibration of machinery, testing protocols, and training processes – anually, this can take months.
AI can simplify this across the board by:
- Translating natural language regulations into step-by-step instructions for line operators
- Converting legal requirements into parameter settings for factory machinery
- Automatically generating staff-friendly, multilingual training materials – without time-intensive workshops
Medical equipment
This industry offers a prime use case for automating manufacturing compliance. Regulations such as the EU Medical Device Regulation (MDR) mandate continuous monitoring of medical devices to ensure functionality in life-critical situations.
One frequent challenge: complaint and service backlogs that risk delayed or missed adverse event reports. That’s what a global medical device manufacturer faced – until they deployed AI.
They implemented an AI-powered complaint evaluation system modeled on their manual workflows and integrated it into their QMS. The system detects anomalies in device usage and settings in real time, automatically classifying incidents under FDA and MDR rules using machine learning models.
As shown in this case study:
- The complaint backlog was completely eliminated
- No regulatory reports were missed
- Manual workload was reduced by approximately 75%
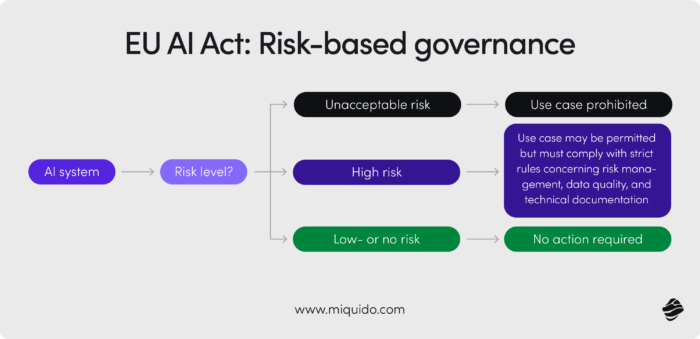
Under the EU AI Act, such AI applications are considered high-risk. Companies operating in or selling to the EU must comply with several mandated measures, including:
- Full traceability and logging of AI activity
- Explainability and auditability of outcomes
- Human oversight mechanisms
- Pre-deployment conformity assessments by notified bodies
It's a considerable effort, but as the stats show, the payoff is significant. In the post-market phase, AI becomes a key ally for ensuring compliance continuity and minimizing business risk. Sensor monitoring, predictive maintenance, audit trails for part traceability.
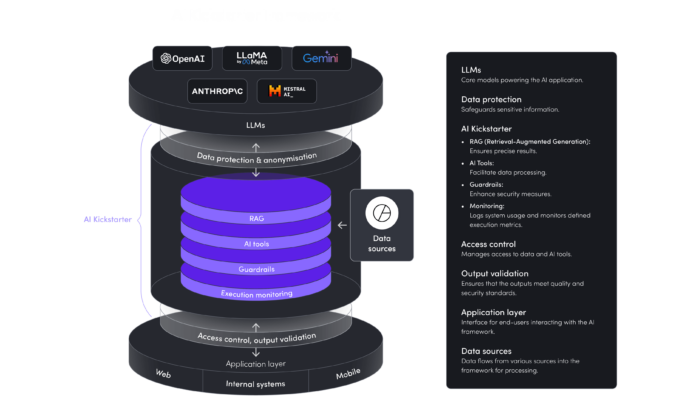
Implementing AI‑driven compliance – step‑by‑step
Planning is crucial in every AI implementation - especially when it comes to compliance. Here's a verified roadmap that will set you for automated compliance success.
Inventory & risk assessment: Map use cases before the regulator does
Before deploying any ai tools, organizations must understand where AI can drive value, and where it can introduce risk. For example, generative AI that drafts technical documentation can accelerate output tenfold, but it might also generate inaccurate or non-compliant content. That’s why it's essential to map specific AI use cases, assign risk ratings (high/medium/low), and align each with compliance frameworks like the EU AI Act or ISO 42001.
Data integration: Connect your systems before AI connects the dots
Compliance teams often work with fragmented data – from ERP and LIMS to PDFs and spreadsheets. Without unified, structured data, even the most advanced ai models will struggle to detect anomalies or provide meaningful recommendations. Seamless data integration ensures traceability, model accuracy, and, critically, trust in AI-assisted compliance decisions.
Pilot AI in key areas: Start where mistakes are most expensive
The best initial ROI comes from applying ai tools in high-volume, high-risk processes, like parsing legal contracts, checking batch deviations, or auditing labeling data. Modern LLMs can compare invoices, technical specs, and regulatory texts automatically, flagging potential compliance gaps before auditors do. Piloting AI in targeted domains also provides a low-risk path to gather feedback, improve models, and build organizational confidence.
Generative AI takes it a step further – it's not just analyzing, it's creating: from drafting risk assessments and audit summaries to generating regulator-ready response templates. In compliance, this can mean hours saved and more accurate documentation with every iteration.
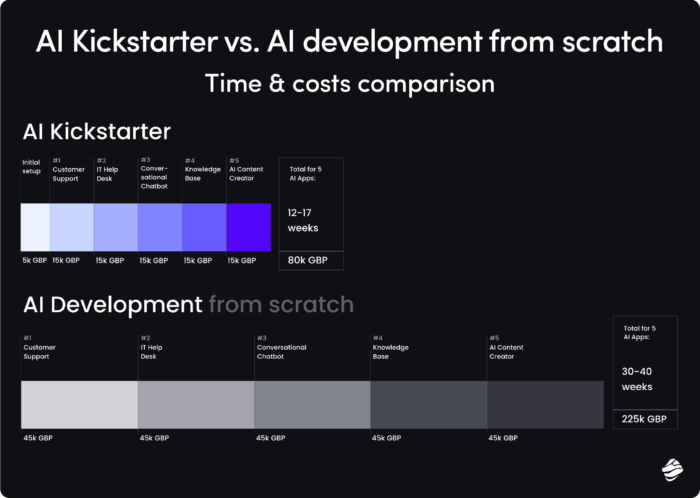
Governance framework: Build oversight before the model makes decisions
Ai risk management starts with a clear governance setup: defined roles, approval workflows for models, and full auditability of every AI-driven output. Human-in-the-loop controls are critical in areas where AI suggestions can have legal or financial consequences. Your compliance teams must be able to understand not only what the model recommends, but why.
Change management: People aren’t the obstacle – they're the engine
No ai tools can deliver value without user adoption. Staff must be trained not just on how to use AI systems, but on how to interpret results, challenge outputs, and escalate when needed. When managed well, change isn't about resistance – it's about empowering compliance teams to co-create smarter, faster workflows.
“AI should support the human in the loop. It’s not about replacing people – it’s about giving them better tools to do their jobs more effectively.”
Kristina Hloptsidis, Chief Innovation Officer at Signify
Continuous monitoring: AI isn’t “set and forget”
To stay compliant with evolving standards, like the EU AI Act deadlines in 2026–2027, AI models must be continuously validated, updated, and retrained. Shifts in regulatory frameworks or data pipelines can cause even high-performing models to drift or fail. That’s why your software partner shouldn’t just deliver a solution—they should deliver a strategy for ongoing monitoring, optimization, and compliance assurance.
Benefits of artificial intelligence in regulatory compliance for different roles
Whether C-level or a part of a technical team, you are impacted by compliance requirements daily. Here's what automation brings to the table.
C-suite: Cut risks before they cut into your valuation
As a decision-maker, you're not just managing business growth – you’re also carrying the weight of reputational, legal, and financial risk. ai technology can help you reduce compliance risks at scale by enabling real time monitoring of anomalies, deviations, or outdated practices—before they snowball into fines or public fallout. With traceable data analytics and audit-ready insights, you'll walk into every board meeting and investor call knowing you're not just compliant, you're ahead.
Technical teams: See it before it breaks
If you're in operations, quality, or IT, you know what it’s like to chase down root causes under pressure, with gaps between MES, LIMS, and spreadsheets slowing you down. ai tools integrated with your tech stack enable real time monitoring of deviations, equipment failures, or process drift, giving you hours or days of lead time. By helping identify patterns in both live and historical data, these systems support better interventions and, more importantly, fewer production surprises.
Compliance officers and managers: Sleep better before the audit
You live in a world of deadlines, evolving regulations, and documents that rarely speak the same language. ai technology helps you automate the tedious, high-stakes tasks, like cross-checking labeling claims against changing local requirements, or building a defensible audit trail from scattered systems. With AI to identify patterns in non-conformities and analyze historical data, your compliance program becomes not only faster, but more proactive, so you can spot gaps before the auditor does.
Legal counsel: Turn uncertainty into defensibility
When enforcement comes knocking, it’s not enough to say you meant to comply—you need documentation that shows you actually did. With ai tools capable of summarizing investigations, tracing actions to data sources, and compiling audit logs, you gain a defensible position in both internal investigations and regulatory reviews. Combine that with deep data analytics and automated alerts on evolving legal risks, and you’re not just reacting—you’re building legal resilience, one case at a time.
EHS and plant safety leads: Less paperwork, more worker safety
You're constantly balancing people, protocols, and pressure to deliver – knowing that a single lapse can put lives at risk. ai technology helps you monitor compliance across shift reports, equipment logs, and incident data in real time, flagging risks like overdue maintenance or safety training gaps. By using AI to identify patterns in injuries or near-misses, you’re not just filling out reports – you’re preventing the next one.
Future outlook on AI tools for manufacturing compliance
Stricter data protection regulations, intensifying data breaches, deepening differences between regulatory standards in different regions - which challenges in adopting AI will impact manufacturers in the following years? Here are some predictions together with actionable insights that will help you benefit from machine learning algorithms in business operations subject to different regulations.
Increasing regulation will redefine “good enough”
With the EU AI Act entering force and U.S. state laws catching up, compliance is no longer just about what’s on paper – it’s about how your systems behave. Whether you’re a compliance officer in life sciences or a GC at a global tech firm, your AI use cases will be judged not only on intent, but also on design, data quality, and traceability. Expect regulators to ask how your models mitigate bias, whether your audit trail includes human sign-off, and if your AI decisions respect GDPR-level transparency in terms of data privacy.
AI won’t just flag problems – it will help fix them
The next evolution of ai technology in compliance won’t stop at detection. Generative systems are already supporting automated remediation: rewriting policy drafts in real time, suggesting corrective actions based on past case law, or even helping compliance teams simulate regulatory scenarios before they unfold. But with power comes risk – llm errors can trigger false flags, or worse, push faulty recommendations – so companies will need to maintain rigorous human oversight, governed workflows, and model-level auditability.
Ecosystem convergence is coming – and it won’t wait
The future isn’t just ai tools in isolation – it’s their convergence with IoT sensors, blockchain ledgers, and cloud-based reporting stacks. Imagine real time monitoring of a cold-chain drug shipment, with blockchain validating every temperature handoff, and an AI system identifying patterns that predict spoilage risk. For pharma, this isn’t a sci-fi scenario – it’s a coming standard, as both DOJ and HHS OIG begin using advanced analytics to uncover potential fraud before it hits the surface.
Pharma’s moment of reckoning is already here
Pharmaceutical companies face a uniquely high-stakes version of this shift. You’re navigating overlapping scrutiny – from the ECCP’s internal controls to the FDA’s evolving stance on AI-enabled technologies. Without formal guidance, you’ll be expected to self-govern: building ai risk management protocols, ensuring privacy across all use cases, and aligning with whatever fragmented, fast-moving standards define your operating jurisdictions. Enforcement agencies already use data analytics to flag inconsistencies – shouldn’t your compliance program be just as smart?
Future-proof your compliance, gain a competitive edge
AI-driven compliance helps you avoid fines, reduce operational risk, and streamline work across roles. Start with a clear assessment, run focused pilots, then scale with confidence.
In a regulatory environment moving fast, staying ahead isn’t optional. It’s strategic. Let’s make compliance your advantage, not your burden.

![[header] ai for manufacturing compliance](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/07/header-ai-for-manufacturing-compliance.jpg)

![[header] top 5 use cases for autonomous delivery in foodtech today](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/08/header-top-5-use-cases-for-autonomous-delivery-in-foodtech-today-432x288.jpg)