The manufacturing sector is undergoing its most significant shift since the early days of industrial automation. What used to be a linear, factory-floor process is now becoming a dynamic, data-driven ecosystem fueled by real-time collaboration, smart infrastructure, and cloud-native technologies.
At the center of this shift is cloud manufacturing, a concept that’s no longer experimental. According to The Business Research Company, the global cloud manufacturing market reached $73.7 billion in 2023, growing at a compound annual rate of 15.6% since 2018. It’s projected to nearly double by 2028, hitting $168.4 billion, and then continue to soar to $353.8 billion by 2033.
As cloud based manufacturing software is going mainstream, companies are looking for a roadmap for its implementation, and this text will help you explore all its angles.
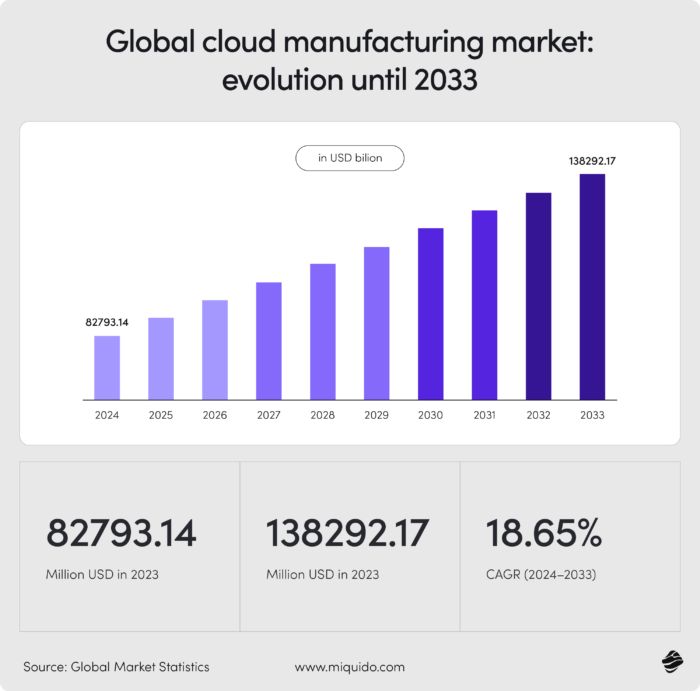
As the market shifts toward flexible, software-defined factories and increasingly global supply networks, the question is no longer if cloud manufacturing will be adopted, but when. Manufacturing organizations delaying this transition are already beginning to feel the friction: ballooning IT overhead, disconnected systems, limited adaptability, and slower go-to-market cycles.
For executives and technical decision-makers, understanding the principles and strategic value of cloud manufacturing is no longer optional. The time to reimagine legacy systems, build resilience, and shift to scalable, cloud-first operations is now – before that gap becomes too expensive to close.
Understanding cloud manufacturing software fundamentals
What is cloud manufacturing?
Cloud manufacturing is a digital model where manufacturing resources – like software, hardware, data, and capabilities –are packaged and delivered as services via cloud platforms. It blends cutting-edge technologies such as IoT, AI, big data analytics, and cyber-physical systems to create on-demand, distributed, and intelligent production environments. This makes it possible to reconfigure operations in real-time, adapt to market shifts, and manage everything from design to distribution on a single digital infrastructure.
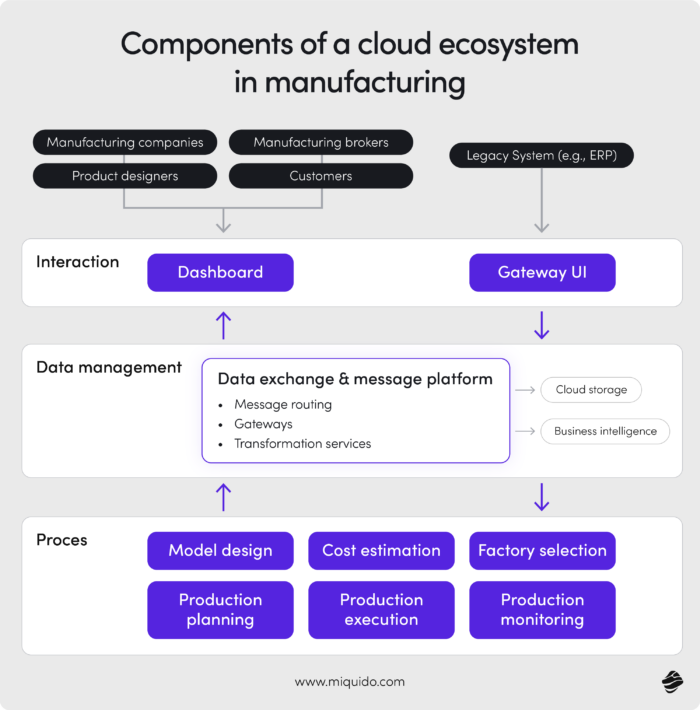
Unlike traditional on-premise systems that are rigid and isolated, cloud manufacturing enables remote access, elastic scalability, and seamless system updates. It also introduces a service-oriented architecture, where various players in the supply chain can plug into a shared digital environment. Whether it's customizing batch production, rerouting orders, or optimizing performance through AI-driven analytics –cloud infrastructure becomes the backbone of the modern smart factory and its manufacturing operations.
Essential components of cloud manufacturing software
Think of cloud manufacturing software as a smart factory's digital nervous system – each component plays a different role, but they only work at full potential when connected. The cloud-based MES tracks everything in real time on the shop floor, while cloud ERP (enterprise resource planning) systems ensure business logic, procurement, and finance stay in sync with production. At the same time, supply chain management platforms align global logistics and materials, creating one connected flow.
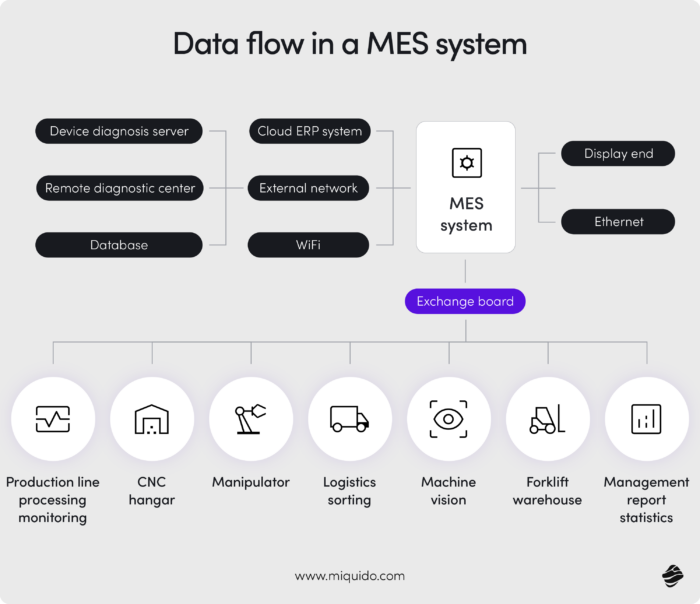
On top of that, cloud-based quality systems help detect, prevent, and document any deviation, while predictive maintenance tools monitor machines to reduce downtime before it happens. Together, these modules form a tight digital loop – analyzing, predicting, and responding without human delay. It's not just software integration; it's operational intelligence delivered as a service.
Cloud computing models for manufacturing
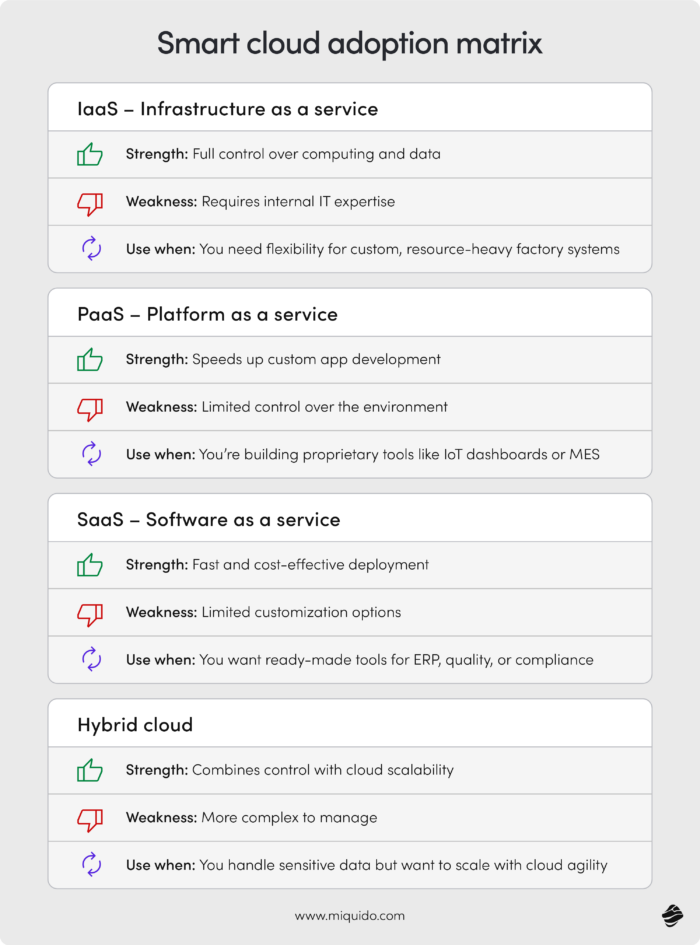
If your company needs full control over computing resources and prefers to tailor every detail of your systems, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) is the way to go. It provides on-demand access to virtual machines, storage, and networking, giving manufacturers the power to build custom manufacturing software from scratch. Just keep in mind: this approach demands solid in-house IT expertise to manage everything internally.
When you're focused on building proprietary apps, like smart dashboards, digital twins, or custom MES layer, Platform as a Service (PaaS) can speed things up significantly. It gives developers all the tools they need without worrying about infrastructure. The trade-off? Slightly less control over the environment your apps live in.
If what you need are ready-made tools you can deploy quickly – for instance, cloud ERP systems, quality trackers, or compliance apps – then Software as a Service (SaaS) delivers the most value. You pay for what you use, avoid heavy upfront investments, and skip the time-consuming rollout. The only limit: less room for deep customization.
For manufacturers who handle sensitive data (like defense, medical, or IP-heavy production) but still want the scalability and speed of the cloud, hybrid models are a strong fit. You can keep critical operations on-premise while running less sensitive workloads in the cloud. It’s a balancing act – but one that gives you both agility and control.
Traditional vs cloud based manufacturing: A comparison
| Category | Traditional Manufacturing | Cloud-Based Manufacturing |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure & Cost | - Physical servers and on-premise data centers - High upfront capital expenditure - Dedicated IT staff for maintenance and updates - Limited scalability and flexibility | - Virtual infrastructure and distributed computing - Pay-as-you-use pricing model - Managed services by cloud providers - Instant scalability and global accessibility |
| Data Management & Analytics | - Siloed data in departmental systems - Limited real-time visibility - Manual reporting and analysis - Restricted data storage capacity | - Centralized data lake architecture - Real-time dashboards and analytics - Automated reporting and insights - Unlimited scalable storage |
| Collaboration & Accessibility | - Location-bound access to systems - Limited remote monitoring capabilities - Restricted supplier/partner integration - Manual communication processes | - Global access from any device - Real-time remote monitoring and control - Seamless partner ecosystem integration - Automated workflow collaboration |
| Maintenance & Updates | - Scheduled downtime for system updates - Manual software installations - Version compatibility issues - Extended support cycles | - Automatic updates with minimal downtime - Continuous feature improvements - Always-current software versions - Proactive security patches |
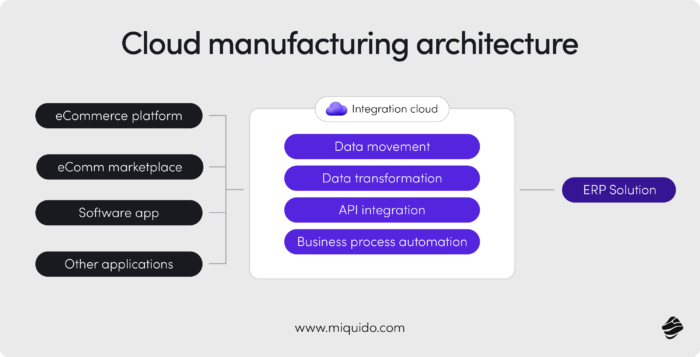
Cloud based systems and industry 4.0 integration
Cloud computing technologies act as the central nervous system of Industry 4.0 manufacturing systems, constantly sensing, analyzing, and coordinating every part of the manufacturing process. Like neurons in the body, cloud-connected systems communicate instantly, ensuring seamless operation across machines, data sources, and decision points. Without this layer of intelligence, the core principles of smart manufacturing would remain fragmented and reactive.
By integrating with IoT devices, the cloud connects machines and sensors across the production line, enabling real-time data collection and analysis. It powers live dashboards that detect anomalies and trigger corrective actions without human intervention. It also makes digital twins and virtual factory models possible, allowing manufacturers to simulate, test, and optimize entire systems before implementing changes in the real world.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning in cloud manufacturing
AI and machine learning in manufacturing industry simply wouldn’t scale without the cloud. The speed, volume, and complexity of industrial data demand flexible infrastructure, real-time processing, and limitless storage – capabilities cloud platforms are built for.
AI-powered predictive maintenance systems depend on cloud platforms to process live sensor data, compare trends, and detect early failure patterns. Machine learning and AI for manufacturing quality control continuously analyzes production data and images to spot defects before they leave the line. In supply chain optimization, cloud-based AI adjusts forecasts and logistics in real time, reacting to demand shifts and disruptions.
Automated decision-making tools rely on cloud integrations to act on insights across MES, ERP, and supplier systems instantly. Even high-resolution computer vision models for defect detection are trained and deployed using cloud GPU infrastructure, something impossible to manage cost-effectively on-premise.
The main challenge lies in ensuring low-latency performance and secure, uninterrupted access to cloud-based data. AI is only as good as the infrastructure that supports it.
Advanced analytics and big data processing
Traditional systems force teams to work with siloed, outdated data. In contrast, cloud-based analytics connects all sources into one live stream, making it possible to monitor, analyze, and act in real time.
Cloud platforms enable real-time production monitoring, letting teams see performance issues as they happen and adjust processes immediately. Predictive analytics in manufacturing improves demand forecasting by blending sales history, market dynamics, and inventory data into one model.
Performance benchmarking becomes frictionless when data from multiple facilities is unified in the cloud, allowing quick comparisons and targeted improvements. Cloud analytics also unlocks cost optimization and operational efficiency, highlighting inefficiencies or waste patterns that would otherwise go unnoticed.
Data requirements and collection strategies
To fully harness the potential of cloud manufacturing, companies must rethink how they handle data. There’s no universal, one-size-fits-all model, but there are proven best practices that can help manufacturers turn raw data into meaningful value. The key lies in identifying the right data sources, setting up reliable infrastructure, and treating data as a strategic asset, not just an operational necessity.
Essential data types for cloud manufacturing
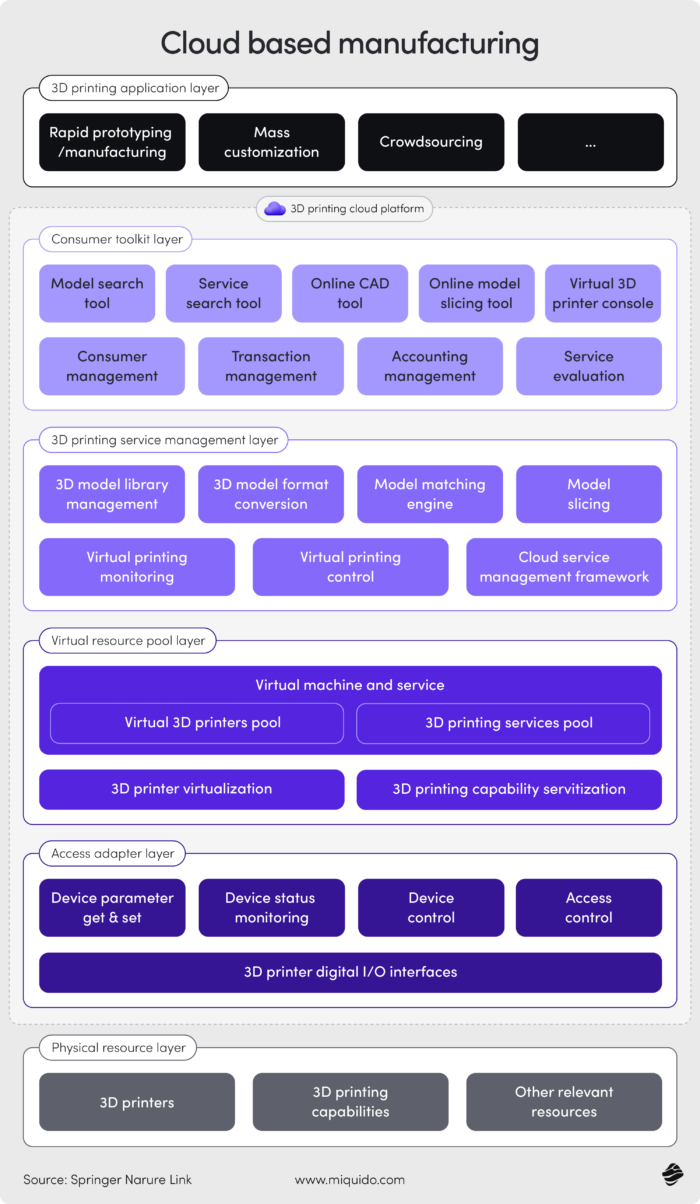
The more data sources you integrate, the clearer the full manufacturing picture becomes. To truly connect the dots, manufacturers need to combine multiple categories of data – each captured through specific layers of the infrastructure.
Production metrics and KPIs are collected through MES platforms and ERP systems, covering cycle times, throughput, scrap rates, and OEE (Overall Equipment Effectiveness). The main challenge here is ensuring consistency across machines and plants that may operate on different standards or systems.
Equipment sensor data and telemetry comes from IoT sensors and edge devices installed on machines, capturing temperature, vibration, wear, and other operational parameters. These signals are rich in detail but often noisy or incomplete, requiring filtering and interpretation before they can be acted on.
Quality control measurements are recorded through specialized QC systems, vision cameras, or manual input stations during or after production. The difficulty lies in aligning subjective, manual checks with automated systems to maintain traceability and accuracy.
Supply chain information is synchronized from ERP systems, supplier APIs, and logistics platforms. It includes lead times, inventory levels, shipment tracking, and procurement statuses – but integration across external sources is often fragmented or inconsistent.
Energy consumption data is gathered via smart meters, factory management systems, and utility APIs. It can be difficult to isolate machine-level consumption from overall plant usage, making it hard to attribute energy waste precisely.
Worker productivity metrics are drawn from MES logs, wearable devices, access control systems, and time-tracking software. These insights are sensitive, and the biggest challenge is balancing transparency with worker privacy and ethical data use.
Data collection infrastructure
Each category of data relies on a specific layer of infrastructure to be collected, processed, and sent to the cloud.
- IoT sensors and edge computing devices capture machine-level telemetry and environmental data directly from the source.
- Manufacturing Execution System (MES) integration enables collection of real-time production processes metrics, quality checkpoints, and process flow data, eventually enabling the use of AI in MES.
- ERP system data synchronization consolidates business data such as inventory, procurement, and supply chain operations.
- Third-party system APIs and connectors bring in logistics, supplier, and utility data, extending visibility across the value chain.
- Manual data entry optimization is crucial for cases where automation isn’t feasible, enhanced through validation rules and smart input interfaces.
Data quality and governance
Good data is the foundation of good decisions. In manufacturing, poor data quality can lead to flawed analytics, incorrect predictions, and costly delays. Data must be accurate, timely, and reliable, especially when it feeds automated systems that drive real-time actions.
The biggest challenge lies in unifying data coming from different machines, systems, and formats. Processes like data cleansing, master data management, and traceability become essential to prevent errors from scaling. Manufacturers also need to stay compliant with industry regulations, ensuring data is handled with proper security, confidentiality, and auditability at every step.
Real-time data processing requirements
In Industry 4.0, reacting to data after the fact is often too late. Real-time processing is what enables manufacturers to stay agile, predictive, and competitive.
- Edge computing for immediate decision-making keeps latency low by processing data directly at the machine level.
- Stream processing for continuous monitoring enables instant alerts, anomaly detection, and automated responses on the shop floor.
- Batch processing for historical analysis supports trend discovery, root cause investigation, and production optimization over time.
- Data warehousing for long-term storage preserves structured data for compliance, audits, and strategic planning.
- Business intelligence and reporting tools transform all of this into actionable dashboards, enabling faster and more confident decision-making across roles.
Implementation and integration process
Transforming a traditional manufacturing setup into a cloud-enabled powerhouse isn’t something that happens overnight. It takes strategic planning, thoughtful design, and a deep understanding of both technology and operations.
The process can feel complex, but with the right partner, it becomes a lot more manageable. Software companies with hands-on experience in manufacturing don’t just offer code – they offer frameworks, insight, and real-world shortcuts that can save months of trial and error.
Assessment and planning phase
- Current state analysis and gap identification
- Technology readiness evaluation
- ROI calculation and business case development
- Timeline and milestone planning
- Stakeholder alignment and change management
Even before the first line of code is written, the planning phase sets the tone for the entire transformation. It’s here that manufacturing businesses uncover gaps, validate technical feasibility, and align their goals across departments. Working with a specialized software partner at this stage helps translate manufacturing complexity into actionable roadmaps, backed by realistic ROI models and clearly defined outcomes.
System architecture design
- Cloud platform selection criteria
- Network infrastructure requirements
- Security architecture planning
- Integration points identification
- Scalability and performance planning
For manufacturers, this step often reveals hidden constraints – from outdated network setups to unclear data flows. Software partners with experience in cloud manufacturing know how to navigate these dependencies and design systems that evolve with your needs, not against them.
Migration strategies
- Phased implementation approach
- Data migration planning and execution
- System integration and testing
- User training and adoption programs
- Go-live and post-implementation support
There’s no single path to migration – only what fits your business best. Whether you're moving one plant or ten, the transition has to be smooth, secure, and non-disruptive. That’s easier said than done. From preserving data integrity to onboarding users, the challenges are real, but entirely solvable with a software partner who understands manufacturing timelines, downtime risks, and the need for clear communication at every phase.
Integration with existing systems
- Legacy system connectivity options
- API development and management
- Data synchronization strategies
- Workflow automation design
- User experience optimization
No system exists in isolation, and manufacturing is full of legacy infrastructure that still holds value. Integration is about finding smart ways to connect the old with the new, without breaking what already works.
This is where experienced software teams can make all the difference: they understand which APIs to build, how to handle data mapping, and where automation will deliver the highest impact with the least friction and align with market demands. The result? Systems that work better together, not harder apart.
Cloud based manufacturing scenarios: Resolving key challenges
No two manufacturers face the exact same transformation journey. The scale of operations, complexity of supply chains and inventory management, and maturity of digital manufacturing infrastructure all play a role in shaping the challenges they’ll encounter when moving to the cloud.
That’s why cloud-based manufacturing can’t rely on a one-size-fits-all model – it has to be tailored to the business it’s powering. Let’s take a closer look at how different types of manufacturers are solving real problems with cloud technologies – and what it takes to get it right.
Large enterprise implementation
Challenge: Complex supply chain optimization across global operations
For large-scale manufacturers operating across continents, coordinating supply chain data is often chaotic. Disparate systems, duplicated datasets, and inconsistent reporting make it nearly impossible to optimize costs or respond in real-time to disruptions.
Solution: Cloud-centric ERP system integration
By centralizing operations on a cloud-based ERP, these enterprises can unify procurement, logistics, and inventory data across all facilities. This real-time visibility turns reactive operations into proactive ones, enabling strategic adjustments before inefficiencies snowball.
Why it works with the right partner:
Integrating ERP at this scale requires more than technical skill – it demands deep knowledge of manufacturing workflows and supply chain intricacies. Top-tier manufacturing software partners bring that understanding, ensuring smoother integrations with minimal operational friction.
Mid-size manufacturer digital transformation
Challenge: Legacy system limitations and data silos
For many mid-sized manufacturers, outdated systems are the biggest barrier to digital transformation. Valuable data is scattered across spreadsheets, proprietary machines, and on-prem databases, blocking automation and analytics.
Solution: Phased cloud migration with AI integration
A phased migration strategy helps bridge the gap. Starting with non-disruptive systems – like quality monitoring or predictive maintenance – companies can gradually introduce cloud services, layering in AI to automate processes and uncover hidden trends.
Why it works with the right partner:
Getting this transition right means balancing modernization with operational continuity. Experienced software teams help structure phased rollouts, integrate AI where it matters most, and future-proof the cloud software without overwhelming internal teams.
Small manufacturer cloud adoption
Challenge: Limited IT resources and capital constraints
Smaller manufacturers often face a different set of issues – lean teams, tight budgets, and little room for infrastructure mistakes. Yet they still need to stay competitive, especially as digital tools become table stakes.
Solution: SaaS-based manufacturing software adoption
Lightweight, subscription-based platforms give small manufacturers access to powerful capabilities –without the upfront costs or need for dedicated IT teams. From inventory to quality tracking, everything runs in the cloud and updates automatically.
Why it works with the right partner:
The challenge here is choosing the right tools and configuring them for fast, tangible results. A software partner with experience in small-batch or niche manufacturing environment can help narrow the focus and avoid feature bloat, delivering real value, fast.
Implementation roadmap and best practices
It’s no secret that digital transformation in manufacturing can feel like a high-stakes leap, especially for small and mid-sized companies. In fact, over 60% of manufacturers cite high upfront costs and financing concerns as their biggest barrier to adopting cloud-based systems. Others nearly half the market—point to data privacy and cybersecurity worries as major obstacles.
These concerns are valid. But they’re not unsolvable.
With a well-structured roadmap – and the right technology partner by your side – it’s possible to address those fears head-on, long before they escalate. That’s exactly where smart implementation makes the difference. Top-tier software providers don’t just deliver code; they act as consulting partners, helping manufacturers align cloud strategies with operational realities.
Here’s what a future-ready rollout typically looks like.
Phase 1: Foundation building
Every smart transformation starts with the groundwork. This phase ensures that your infrastructure is stable, secure, and ready for what’s next.
- Infrastructure assessment and planning
Identify what’s in place and what’s missing, building a roadmap that minimizes disruptions while maximizing long-term ROI. - Cloud platform selection and setup
Choose the platform that aligns best with your business needs – not just today, but two, five, and ten years from now. - Basic connectivity and security implementation
From VPN protocols to firewalls to secure user authentication, this is where cybersecurity becomes baked into the process, not bolted on. - Initial user training and change management
Prepare your team for the road ahead, turning hesitation into buy-in through structured onboarding and clear communication.
Why a partner helps:
Early-stage missteps are costly, but avoidable. An experienced software partner helps streamline compliance, reduce infrastructure bloat, and build cloud based platforms that grow with your business.
Phase 2: Core system migration
With the basics in place, it’s time to bring your core systems into the cloud – securely, systematically, and without breaking existing workflows.
- Critical system migration and integration
Shift ERP, MES, and other essential tools to the cloud in a way that preserves continuity and minimizes downtime. - Data migration and validation
Ensure that legacy data is not only transferred but also cleansed, normalized, and optimized for use in the new environment. - User acceptance testing and feedback
Pilot testing confirms everything is working as intended, while real feedback helps fine-tune systems before full rollout. - Performance optimization and tuning
Remove bottlenecks and fine-tune configurations to match actual production needs, not just theoretical ones.
Why a partner helps:
This is the most technically demanding part of the journey. The right partner brings deep industry experience, making sure integrations are fast, reliable, and aligned with how your shop floor actually operates.
Phase 3: Advanced features and analytics
Now that the foundation is strong, it’s time to unlock the real power of cloud: intelligence, automation, and data-driven performance.
- AI and machine learning implementation
From predictive maintenance to intelligent scheduling, AI capabilities turn data into action and unlock serious competitive advantage. - Advanced analytics and reporting
Custom dashboards help monitor KPIs in real time and surface trends you didn’t know existed. - Process automation and optimization
Reduce manual tasks, cut down on errors, and let systems handle the repetitive work – at scale. - Full user adoption and training completion
Make sure everyone is not only trained, but confident in using the new tools daily.
Why a partner helps:
Many manufacturers stop short of this phase. A good partner ensures that the investment keeps paying off – guiding you from data collection to real intelligence, with minimal friction.
Phase 4: Continuous improvement (Ongoing)
Cloud manufacturing doesn’t have an endpoint – it evolves with your business. This final phase focuses on keeping systems sharp, secure, and strategically aligned over time.
- Performance monitoring and optimization
Regular check-ins ensure systems stay aligned with changing production demands. - Regular security assessments and updates
Proactive audits help you stay ahead of evolving threats and compliance requirements. - Feature enhancement and expansion
Add new capabilities as your business grows – without starting from scratch. - ROI measurement and reporting
Tie digital investments back to hard numbers, showing clear business value at every stage.
Why a partner helps:
Sustaining performance is just as important as reaching it. A long-term partner helps continuously adapt the system, optimize ROI, and act as your innovation sounding board as the industry evolves, along with data security challenges and changes in customer demand.
With a thoughtful roadmap aligned with your business processes and the right support, cloud-based manufacturing doesn’t have to be risky, overwhelming, or expensive. It can be smart, scalable, and surprisingly affordable—especially when built on a foundation that’s been proven to work.
Want to explore what your tailored roadmap might look like? Let’s outline it together.

![[header] cloud based manufacturing maximize efficiency](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/header-cloud-based-manufacturing_-maximize-efficiency.jpg)

![[header] ai in manufacturing execution systems – use cases](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/header-ai-in-manufacturing-execution-systems-–-use-cases-432x288.jpg)
![[header] e business integration in manufacturing – 2024 statistics](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/header-e-business-integration-in-manufacturing-–-2024-statistics-432x288.jpg)
![[header] exploring the key benefits of ai in manufacturing industry](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/04/header-exploring-the-key-benefits-of-ai-in-manufacturing-industry-432x288.jpg)