Pretty much every business across every industry collects data. Email addresses, billing information, website visits, employee records, sales data, supply chain management – the list goes on. And there’s a reason data is so widely collected. Every business recognises it as valuable. Data isn’t inherently valuable on its own, however. Data becomes useful to businesses when it is used to make decisions. That’s where business intelligence and data science come in. Both are methods of working with data to transform business operations and help create an effective business strategy. Still, they come with distinctions that it is important to understand to ensure you are using them correctly for your business.
What is Business Intelligence?
The main components of business intelligence are analysis, insight, action, and measurement. Business data is collected, analysed and visualised; meaningful and effective insights are garnered from this information; insight-led decisions are made based on this; and the results are measured against competitors or historical data.
Typically, business intelligence is achieved through a collection of technologies, applications and processes that work together to present business data in an organised, meaningful and actionable way that is accessible to all users.
Here’s an example of how business intelligence can be used:
Key business intelligence terms
To understand business intelligence further, get familiar with some of these key terms.
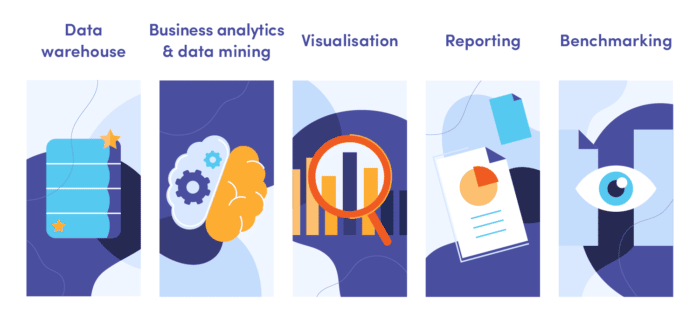
Data warehouse
A data warehouse is a system that stores company information from a variety of places in one, centralised and accessible location. Data warehouses are key to business intelligence as they enable data from different sources across the business to be analysed and reported on so that it can be converted into meaningful insights.
Data warehouses usually consist of data from different areas of the business: HR, Marketing, Sales, Finance from all sorts of operational systems: CRM, billing, mailing lists and so on.
Business analytics and data mining
Once the data is in the data warehouse, it can then be analysed and mined by business analytics tools. Data mining uses a combination of databases, statistics and machine learning to uncover trends and patterns in the data.
Visualisation
Once these tools have extracted useful information from the data, a user interface (usually an interactive dashboard) can be used to visualise the information. Charts, graphs and diagrams all help to present the data in a way that helps it become meaningful and easier to comprehend.
Reporting
The data analysis and visualisation can then be shared amongst key stakeholders in the business so that they can spot key business insights and make decisions toward business goals.
Benchmarking
Part of business intelligence is benchmarking current data with historical data to track changes and performance against the business’s objectives. Benchmarking can also be done against industry standards and competitors, providing another level of insight on what is successful and what can be improved.
Business intelligence tools
Contemporary business intelligence tools are made to be interactive, self-serving and accessible. Whereas historically IT departments managed all access to data, business intelligence today typically allows all levels of users to create dashboards and reports depending on their needs. Business intelligence tools empower individuals to answer their own questions without relying on the help of experts to understand the data.
Popular business intelligence tools include Sisense, Microsoft Power BI, Yellowfin, Domo, Tableau and Looker but there are many, many more!
What is Data Science?
Data science is similar in many ways to business intelligence. Much like the latter, data science works to convert data into useful information to positively influence business decisions by making them more informed and factually-based. To convert this data into actionable information, data science uses a combination of scientific methods, processes, mathematical tools, statistics, algorithms and ML solutions. Much like business intelligence, it looks to find hidden patterns and trends, using the conclusions to take informed actions.
However, unlike business intelligence which focuses solely on structured data, data science deals with both structured and unstructured data. Structured data refers to data that is stored in a pre-defined format, is organised and fits into spreadsheets. It’s accessible, easy to use and easy to decipher with machine learning algorithms. Unstructured data is the opposite and can’t be processed with usual methods or tools. It’s data in its raw form so it requires expertise to be analysed. That’s where data science comes in.
Data science is typically considered more future-focused than business intelligence. It focuses on asking ‘what if’ questions and making future predictions, while business intelligence focuses more on what’s happened in the past and is happening in the present. Being future-based and predictive, data science allows businesses to prepare for future events, trends and opportunities.
Here’s a data science application example:
Key data science terms
Data science is an expanding and evolving field. Understand some of the key terms below.
Machine learning
Machine learning refers to when computers mimic human learning. Computers use data to learn from examples and then make predictions or exhibit behaviour based on it. For example, Amazon Alexa and other voice assistants learn from the data it collects, such as your daily alarms, to make recommendations to you based on them.
Artificial intelligence
Machine learning is a subcategory of artificial intelligence. Artificial intelligence (AI) as a term was created by Stanford Professor, John McCarthy, who defined it as “the science and engineering of making intelligent machines.” AI in data science refers to creating systems that can intelligently solve complex problems from data, learn from them and make decisions.
Check out our blog on how to use Artificial Intelligence in eCommerce.
Data analytics and data mining
Data analytics is the process of collecting data and analysing it in order to make more informed business decisions. Data mining is a technique used to predict future trends by studying existing ones. Both are key components of data science.
Big data
Big data is huge data sets that are analysed using computers to reveal trends and patterns. Big data is the data that is so complex that conventional data management tools can’t be used to store or process it. Big data holds more information, which makes it useful for planning and strategy. Big data can be used with machine learning to accelerate the process of uncovering and analysing key trends.
Data science tools
There are a number of popular tools used in the field of data science that can be used for data visualisation, statistical programming languages, algorithms, databases and more. Here are some of the most used ones today: SAS, Python, Integrate.io, Rapid Miner, DataRobot, Trifacta, Tableau, Amazon Lex.
What’s the difference between business intelligence and data science?
While at first glance, business intelligence and data science seem very familiar, there are a number of distinct differences that make each suited for different purposes.
| Business Intelligence | Data Science | |
|---|---|---|
| Time focus | Past and present Business intelligence looks at things that have happened in the past – previous performance and/or events – to inform decision-making. | Future Data science looks towards the future and predicts what is most likely to happen next to determine what the best course of action is. |
| Data types | Structured Business intelligence works only with structured data: clearly structured, quantitative, searchable data. | Structured and unstructured Data science works with both structured and unstructured data – which is qualitative, stored in its native format and requires more work to be processed. |
| Approach | Descriptive, comparative Business intelligence’s approach involves looking at visualisations of what’s already happened and comparing it to the present and competitor data to draw conclusions about performance. | Explorative, experimentative Data science investigates what is likely to happen in the future using hypothesis testing and exploring trends. |
| Deliverables | Reports, dashboards and ad hoc Reports and dashboards primarily make up all of the deliverables from business intelligence, as well as responses to ad hoc requests. | Statistical / predictive models and hypothesis testing Data science deliverables include custom-built models that predict future events and trends. |
| Key purpose | Help make informed decisions and drive action Both business intelligence and data science help drive better decisions that are informed by data. They focus on driving action towards goals, by arming businesses with valuable information. | |
| Characteristic | Responsive Business intelligence is a responsive process, meaning that it helps decision making based on what’s happened previously. If a business had greater website traffic during a sale, it could hold more sales in the months where traffic is typically low. | Preemptive Data science is preemptive – it makes sure the business is ready for future events to come. It predicts what will happen in the future to help define business strategy. |
Summary
It’s clear that the lines between what is business intelligence and what is data science are very blurred. Both processes overlap in their purpose to empower decision makers with useful, valuable information. While business intelligence analyst informs actions by looking at past performance, data science predicts the future and tests hypotheses by analysing key data trends and patterns. When it comes to business intelligence vs data science, it is not a case of ‘which one is better?’ but instead an appreciation of the key benefits and distinctions of each. Incorporating both into your business strategy will help inform decisions comprehensively by encompassing data based on the past, present and future.
Partner with us to revolutionise your business strategy today with data-driven decision making. Take advantage of our expert Business Intelligence and Data Science consulting services and work with us to create a tailored solution that will help you meet your business goals faster and more effectively.