Although individual manufacturing niches differ in virtually everything — from production specifics to the supply chain — they all share one common aspect: quality control requires the implementation of highly complex measures. Every medicine, every snack, every electric appliance that makes its way to a store shelf must meet a wide range of requirements.
Some of these requirements stem from the manufacturer’s internal policies, while others are dictated by industry-specific regulations, safety standards, or distributor expectations. For example:
- Medical device manufacturers must comply with regulations set by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) in the US or MDR (Medical Device Regulation) in the EU.
- Meat producers are subject to standards imposed by bodies like the USDA (United States Department of Agriculture) or EFSA (European Food Safety Authority).
- Technology companies need to meet norms such as ISO 9001, RoHS (Restriction of Hazardous Substances), and CE marking in Europe.
Beyond regulatory compliance, quality control processes serve another crucial function — they ensure consistency in quality, which is vital for maintaining steady sales. When it comes to components used in electronics or machinery, for example, even a millimeter's deviation can render the entire product unusable.
So how can manufacturers ensure that every item leaving the production line is free from defects, meets customer expectations, and complies with relevant regulations? Without AI, achieving these goals is extremely difficult — and in this article, we’ll take a closer look at how different companies are leveraging AI to power their quality control strategies. Discover why quality control is one of the top AI use cases in manufacturing.
Why AI makes a difference in quality control processes?
Not too long ago, quality control was a painstaking, manual process. Teams of inspectors stood beside production lines, visually scanning products for defects, checking dimensions with calipers, or performing spot checks using checklists taped to clipboards.
This approach was time-consuming, prone to fatigue-driven errors, and often inconsistent — especially across multiple shifts or facilities. It wasn’t uncommon for entire batches to be rejected late in the process or, worse, for flawed products to reach customers, resulting in complaints, recalls, and reputational damage.
Today, the picture looks entirely different - at least among the leaders of digital integration in manufacturing. With AI systems embedded in quality control processes across the entire supply chain, many of the traditional pain points are not just improved, but eliminated. Visual inspections are now performed by machine vision systems that never tire. Data from sensors is analyzed in real time to detect patterns invisible to the human eye. Quality standards are monitored continuously, not just periodically.
The result? Fewer defects, faster reactions, and a level of consistency that manual systems simply couldn’t match.
Overcoming the limits of human perception, focus, and attention to detail
Studies show that human inspectors can miss up to 20–30% of visual defects when fatigue sets in — especially during repetitive tasks. AI-powered vision systems, on the other hand, maintain 100% attention and precision, scanning each item with the same level of focus whether it's the first or the ten-thousandth on the line. This not only improves defect detection rates but also ensures a more objective and standardized assessment.
Scaling quality without scaling costs
Where traditional quality control required more human inspectors to scale with production, AI scales effortlessly. Whether you're producing 1,000 or 100,000 units, the same AI model can handle the workload without compromising accuracy or requiring overtime pay.
Real-time insights instead of post-hoc analysis
In a manual system, quality issues are often discovered after production is complete. AI flips that script — enabling real-time alerts and immediate process adjustments. This prevents entire defective batches from being produced and helps teams make smarter, faster decisions on the spot.
AI in manufacturing quality control: practical use cases of artificial intelligence and machine learning across industries
To understand the benefits of AI in manufacturing quality control and assessment, it's worth looking at real-world examples from specific industries. A quick scan of the market makes it immediately clear that viewing AI as a risky enhancement is largely a thing of the past.
Why? Because manufacturers operating in high-responsibility sectors — where products serve critical functions and are subject to strict regulations — are now leading the way in adopting AI for quality control. In industries where extreme precision is essential and the stakes are high due to the risk of heavy penalties, AI functions as a protective shield.
Let’s take a closer look at a few key industries to understand their specific challenges related to quality control and how they’ve integrated AI solutions. The real-life examples we’ve gathered show just how profitable switching to this form of quality management can be.
AI for quality control processes in pharmaceutical industry
In the manufacturing industry, defects in the production process can lead to a wide range of consequences. Most commonly, they result in financial losses and damage to a company's reputation. However, in highly regulated sectors like pharmaceuticals, such issues can escalate into serious health and safety hazards. This makes advanced quality control and quality assessment not just beneficial but absolutely essential.
And yet, ensuring high-quality standards is no simple task. One common risk during the manufacturing process is cross-contamination of the drug. The causes vary—from improperly cleaned components on the production line, to gaps in automation and robotic systems.
How AI is used to detect defects in drugs in real time with GenAI at Merck
While prevention remains the gold standard, modern solutions like AI quality control are transforming how companies approach quality assurance. AI driven systems facilitate the detection of incorrect dosing, wrong products in the batch, drug degradation and other issues common in medical manufacturing.
A compelling example comes from Merck, which leverages machine learning and real-time data analysis to revolutionize its quality control processes. By integrating a combination of AWS services with cutting-edge generative AI techniques, Merck analyzes defects in life-saving drugs more efficiently. They use Gen AI models, such as GANs and Variational Autoencoders, to simulate production scenarios by generating synthetic images of complex defects. This addresses a major challenge: limited access to sufficient training data for rare or nuanced defects.

The impact? Game-changing—both in terms of safety and cost. As Christophe Martin, Quality Unit Director at Merck Serono, explains, their production processes previously encountered 1 to 5 deviations daily, with about 100 cases under investigation at any given time. These deviations could halt production entirely. And while many deviations flagged as potentially major turned out to be minor, the resulting downtime and investigative costs were significant.
Thanks to the new AI-driven process, Merck has dramatically reduced unnecessary shutdowns and investigation cycles. This is a shining example of how machine learning and AI-powered quality control can redefine standards in the manufacturing industry.
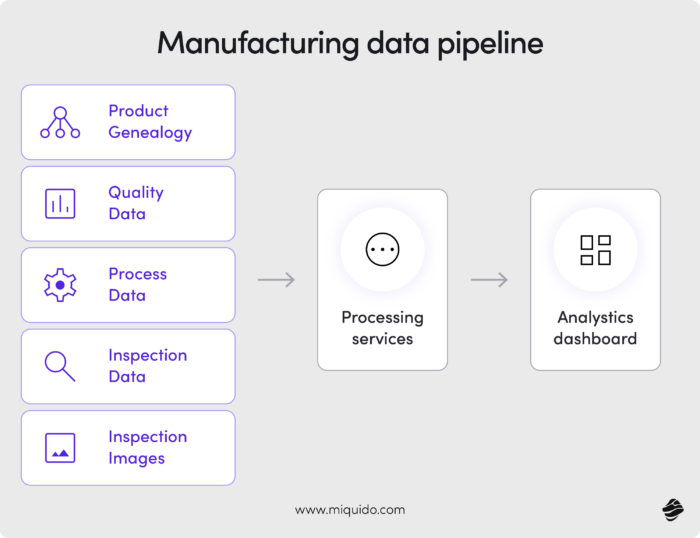
When we talk about quality control in medicine manufacturing, our minds often go straight to the chemical composition of the substances and raw materials themselves. But just as critical—though sometimes overlooked—is the detection of defects in packaging and the critical information displayed on it.
In the pharmaceutical industry, packaging must be airtight, compliant with strict regulations, and clearly labeled. Even a small printing error can render essential information—such as dosage instructions or the concentration of an active ingredient—unreadable. That’s a serious risk, both from a safety and compliance standpoint.
This is where AI-powered computer vision outperforms the human eye. In a fraction of a second, it can detect missing elements, smudged prints, or incorrect label placement. It verifies that both the product and its packaging meet rigorous quality standards, such as ICH Q10 (the international pharmaceutical quality management standard) and GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice).
Major pharmaceutical companies like Pfizer are already tapping into this potential, integrating advanced computer vision systems into their manufacturing processes. Other global pharma players are also preparing to adopt similar innovations, recognizing that the future of quality control goes far beyond what's visible at first glance.
AI-driven quality control in automotive industry
The automotive industry demands a particularly rigorous approach to quality control due to the extreme complexity of its products. A single vehicle consists of thousands of interconnected components—mechanical, electrical, and software-based—all of which must function flawlessly together to ensure safety and performance. Any defect, even in a minor part, can lead to critical failures such as brake malfunction, electronic system errors, or structural weaknesses, posing serious risks to both passengers and other road users.
How artificial intelligence is used in component inspection by BMW
BMW is harnessing the power of AI-driven vision systems to inspect vehicle bodies with exceptional precision. By analyzing images in real time, these systems can detect surface defects such as scratches and dents—often with greater accuracy than human inspectors.
Regulatory standards add further complexity to quality assessment in the automotive sector. The IATF 16949 standard, a global benchmark for automotive quality management, mandates continuous improvement, defect prevention, and reduction of process variation. Artificial intelligence supports these goals by enabling predictive quality control and processing sensor and equipment data to improve production efficiency.

How Ford uses AI to optimize torque converter assembly
Following BMW’s use of AI in body inspection, Ford demonstrates another compelling application—this time in assembly optimization. At its Livonia plant, Ford employs AI technology from Symbio Robotics to streamline the installation of torque converters. The system learns from previous assembly attempts by analyzing motion data, enabling robotic arms to perform more efficiently. As a result, this stage of production has been accelerated by 15%, showcasing how AI is not only improving quality control but also boosting productivity in the automotive manufacturing process.
Why AI in automotive quality control is more crucial than ever
Given the rapid evolution of the automotive industry, AI in quality control is more necessary than ever. The shift toward electric vehicles (EVs) is forcing manufacturers to adapt their production processes to new requirements and safety considerations.
With the rise of electric sustainability come new challenges. EV batteries, under specific conditions, are at risk of severe, hard-to-extinguish fires—necessitating preventive design and strict inspection standards. Additionally, the heavy reliance on complex electronic systems introduces another layer of risk, demanding the use of AI-based diagnostics and automated testing systems to ensure functionality and compliance.
Most traditional automakers have launched dedicated EV assembly lines, but every new production process carries an increased risk of defects. That’s why AI-driven inspection and predictive analytics are becoming foundational tools in maintaining safety, compliance, and competitiveness in this rapidly changing industry.
Manufacturing quality control in medical equipment production
A great example of AI's potential in quality assessment is the medical equipment production industry. Beyond the complexity of the devices themselves, manufacturers face a critical challenge: minimizing product defects and vulnerabilities is essential, as any malfunction can pose serious risks to patient health and safety.
For this reason, the sector is heavily regulated. Globally, companies must comply with ISO 13485 (quality management systems) and ISO 14971 (risk management), while in the U.S., FDA regulations require continuous monitoring of device accuracy even after market clearance. This creates a demand for robust quality systems, real-time process data tracking, and proactive issue detection—challenges that are difficult to address with manual methods alone.
This is where AI algorithms and machine learning models can transform operations. They enable manufacturers to automate performance monitoring, implement predictive maintenance, and quickly identify defects or anomalies on production lines. These technologies not only streamline compliance with stringent regulations but also help reduce risk, improve supply chain transparency, and boost overall production efficiency.
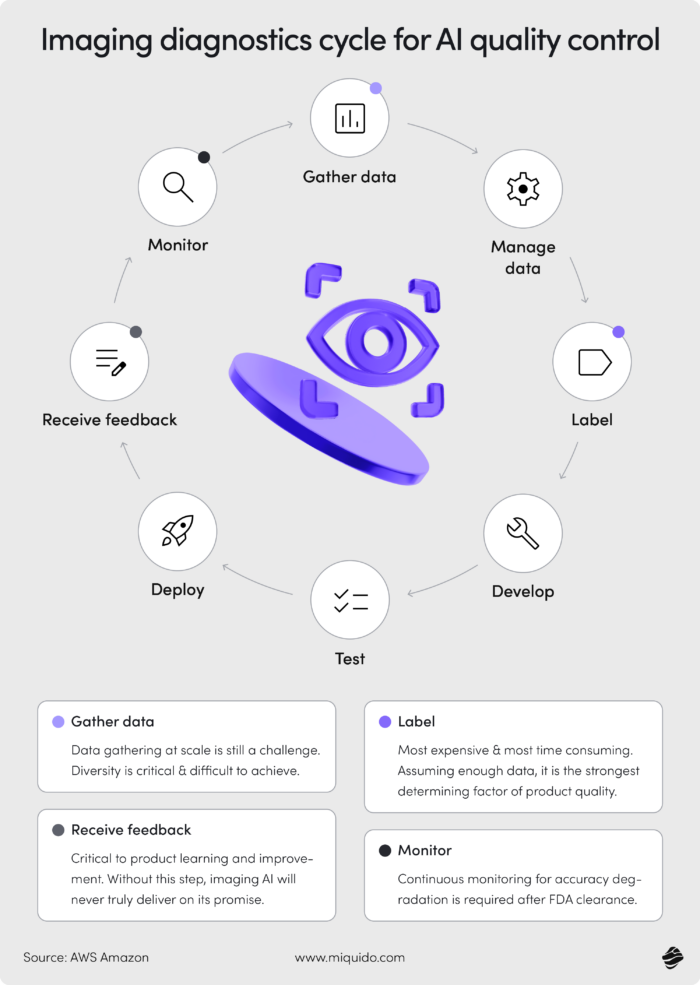
AI in medical equipment production is classified as high-risk in the EU
According to the AI Act, adopted in 2024, the use of AI in medical device manufacturing is classified as high-risk, which imposes additional requirements for transparency, oversight, and risk management. To ensure compliance and avoid violations of EU law, partnering with an experienced AI implementation provider is crucial.
How AI helped MPE, Inc. eliminate costly quality issues
A strong real-world example of using AI in medical equipment quality assessment is MPE, Inc., a U.S.-based manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, specializing in designing and producing healthcare devices. The company began using AI after receiving frequent complaints from clients about missing components in delivered equipment. Traditional quality control methods based on manual inspection and checklists failed to detect these product defects.
By implementing a deep learning-based image analysis solution, MPE gained the ability to automatically detect missing or incorrect parts on the assembly line. If issues occur, archived images of each assembled unit allow for quick verification. The result? Reduced costs, improved customer relationships, and greater production efficiency—all while maintaining high compliance with regulatory standards.
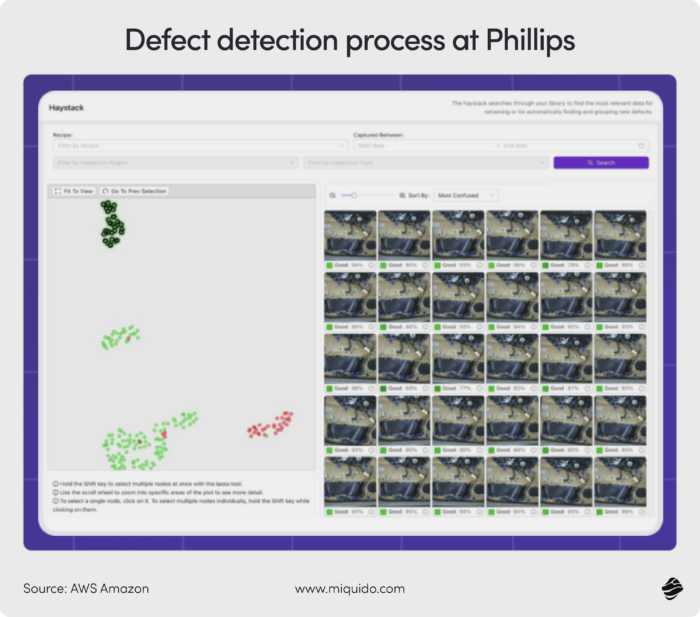
Manufacturing quality control in aviation industry
Just like medical equipment, aircraft require continuous inspections even after entering the market. Aviation regulations mandate that every operational aircraft undergo regular, rigorous checks to ensure ongoing airworthiness and safety. This inspection process is governed not only by international standards such as AS9100—the aerospace quality management standard—but also by local aviation laws.
Increasing pressure, rising standards in the aviation industry
With the industry going under growing scrutiny, innovations in quality control are more important than ever. In May 2024, President Biden signed the FAA Reauthorization Act of 2024, a sweeping $105 billion package aimed at enhancing aviation safety and consumer protections. Among the most impactful changes are increased FAA oversight, more safety inspectors on production floors, and stricter quality standards for manufacturers.
The consequences were immediate for Boeing. After a string of incidents involving the 737 MAX, the FAA required the company to create a comprehensive plan to address systemic quality control issues. With several aerospace incidents in the US between 2024 and 2025, pressure on manufacturers is likely to intensify.
In this high-stakes environment, AI is emerging as a game-changing ally. Its ability to detect subtle patterns and predict failures before they happen can drive significant improvements in safety and reliability. After all, aviation incidents are rarely due to a single issue—it's the accumulation of overlooked or complex faults.
AI-powered drones by Donecle revolutionizing aircraft inspections
To improve the overall operational efficiency and accuracy of inspections, many manufacturers are turning to AI. A standout example is Donecle, a French company pioneering the use of autonomous drones equipped with AI for external aircraft inspections. These systems analyze images in real time, detecting damage such as cracks or lightning strikes with exceptional precision. This not only speeds up the inspection process but also boosts its consistency and reliability.
Given the intricacy of aircraft structures, traditional inspections are time-consuming and prone to human error. AI-driven drones address these challenges head-on, enhancing both safety and efficiency.

Cut costs and improve accuracy with AI quality control
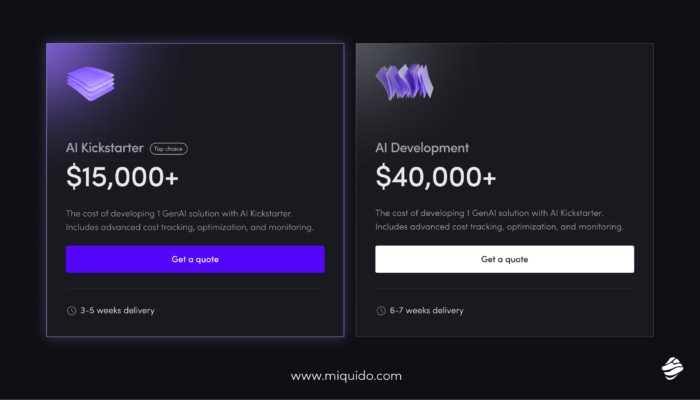
Since AI proves effective in such demanding niches, it can help any company in the manufacturing industry. The key is having an experienced partner in developing custom manufacturing software and a deep understanding of the regulations and quality standards that are crucial to your business. Let's talk about them and find a solution with a fast ROI. In certain areas, our AI Kickstarter framework cuts GenAI development costs by 60% on average.

![[header] ai for manufacturing quality control](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/05/header-ai-for-manufacturing-quality-control.jpg)