While AI has been a buzzword for a while, the emergence of technologies like ChatGPT has thrust Generative AI (Gen AI) into the spotlight. Many assume they’re just different names for the same futuristic tech. However, the reality is much more layered, especially when we consider the role of artificial intelligence in business. As we unravel these technologies, we’ll discover not just their definitions but their distinct impacts and potentials.
In this guide, we’ll explore:
- AI and Generative AI Defined: Cutting through the jargon to what matters.
- Evolution and Technology: From history to the core tech that sets them apart.
- Capabilities and Applications: Understanding their unique strengths and uses.
- Industry Transformations: How they’re reshaping various sectors.
- Looking Ahead: Future trends, ethical considerations, and choosing the right tech.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a branch of computer science dedicated to creating machines capable of intelligent behavior. It’s the science of designing smart algorithms and systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. This includes problem-solving, recognizing speech, translating languages, and decision-making. AI ranges from your smartphone’s voice assistant to complex algorithms that drive decision-making in finance and healthcare.
What is Generative AI (Gen AI)?
Generative AI (Gen AI) represents the next step in the evolution of AI. It’s a subset of AI focused on creating new and original content. Unlike traditional AI systems, which operate based on pre-existing data and rules, Generative AI generates new data and ideas, from digital art to novel text compositions. It uses advanced machine learning techniques, like deep learning, to not just analyze but also produce content that is creative and contextually relevant.
AI’s Journey to Gen AI
The transition from AI to Generative AI is a key milestone in the history of technology. AI’s roots trace back to the 1950s, with the development of simple neural networks and the Turing Test, designed to evaluate a machine’s ability to exhibit intelligent behavior. However, it wasn’t until the rise of big data and advanced computational power in the 21st century that AI truly began to flourish.
Significant developments include:
- Deep Blue and Chess: In 1997, IBM’s Deep Blue became the first computer system to defeat a reigning world chess champion, Garry Kasparov, showcasing the potential of AI in complex problem-solving.
- Deep Learning Revolution: The 2010s saw a surge in deep learning, a subset of machine learning based on artificial neural networks. This transformed AI’s capabilities, especially in image and speech recognition.
- Rise of Generative Models: The mid-2010s witnessed the emergence of generative AI models like GANs (Generative Adversarial Networks), which could create realistic images and artworks.
- Language Processing Breakthroughs: Tools like OpenAI’s GPT-3, introduced in 2020, marked a significant leap in natural language processing and generation, offering capabilities from writing essays to coding.
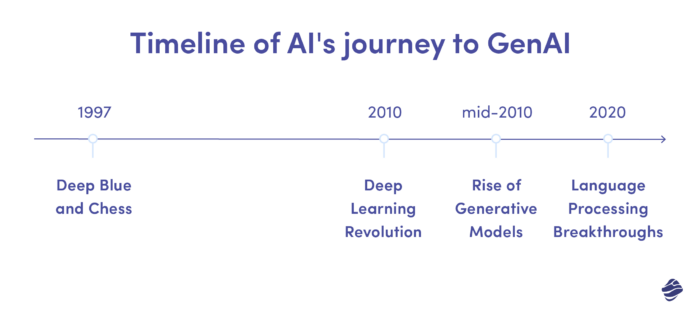
These milestones illustrate AI’s transformation from a rule-based system to an adaptive, creative force. Today, Generative AI is not just a tool for automation but a catalyst for innovation, reshaping industries from entertainment to healthcare.
Generative AI vs traditional AI: Technology and Algorithms
Now that we’ve covered the foundations, it’s time to discuss the difference between AI and Gen AI in terms of their technological frameworks and algorithms. To fully grasp Gen AI, one must first understand how does AI work. This foundational knowledge not only illuminates the intricacies of AI but also helps in understanding the complex technology of Generative AI.
Traditional AI Focuses:
AI’s functionality is built on a foundation of diverse algorithms, each crafted to execute distinct tasks effectively.
Traditional AI systems often employ decision trees that mirror human decision-making, showcasing how AI can replicate our logical processes. These systems excel in identifying underlying patterns in data, a cornerstone in AI’s ability to simulate human-like decision-making.
Machine Learning: A Core Component
A substantial portion of AI’s prowess lies in machine learning solutions. These algorithms, using training data, are trained to recognize patterns and make data-driven decisions. Techniques like logistic regression analysis and support vector machines are integral in this sphere, allowing AI to learn from and adapt to new data. The use of labeled data in supervised learning scenarios is a classic example, where AI is trained to identify and categorize data based on predefined labels.
Neural Networks: Advanced Pattern Recognition
Delving deeper, neural networks represent an advanced tier of AI, crucial in fields like. These structures are designed to mimic the human brain’s ability to recognize and interpret complex patterns. They play a crucial role in tasks involving the processing of extensive sensory data, such as in image and speech recognition. Neural networks’ ability to process and analyze large datasets makes them invaluable in extracting meaningful insights from intricate data structures.
Generative AI Algorithms:
Generative AI stands apart from traditional AI, including forms of weak AI that are designed for narrow, specific tasks. Gen AI focuses on a broader and more dynamic range of capabilities. It transcends simple data processing, venturing into the realm of creating novel and original content. This shift from mere data interpretation to content creation marks a significant evolution in the AI landscape.

Deep Learning: The Backbone of Gen AI
Deep learning plays a critical role in Gen AI. As an advanced subset of machine learning, it employs multi-layered neural networks that can process and learn from vast amounts of unstructured data, such as texts and images. This capability is central to Gen AI’s ability to analyze and generate complex data patterns, making it a powerful tool in data science and content creation.
Generative Models: GANs and VAEs
At the forefront of Gen AI are generative models like Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs). GANs, for example, use two ANNs in a generative-discriminative interplay, significantly expanding the possibilities of what AI can achieve. This unique mechanism allows GANs to generate highly refined and sophisticated outputs, a process that is central to the innovative nature of Gen AI.
Contrasting the Technological Frameworks of AI and Gen AI
The key distinction between AI and Gen AI lies in the complexity and objectives of their algorithms.
- AI’s Structured Approach: Traditional AI excels in analysis, decision-making, and predictive modeling, thriving in environments where objectives and parameters are clearly defined. This structured approach is evident in applications ranging from data analysis to complex automated systems.
- Gen AI’s Creative Frontier: In contrast, Generative AI focuses on more dynamic and creative domains. They are designed to not only analyze existing data but also to use it as a foundation for generating new, innovative outputs. This requires a higher degree of adaptability and advanced learning capabilities, setting Gen AI apart as a tool for innovation and creation.
AI and Generative AI Use Cases
Understanding the practical applications of AI and discovering Generative AI use cases helps illustrate their transformative impacts, demonstrating how they solve real-world problems across various domains.
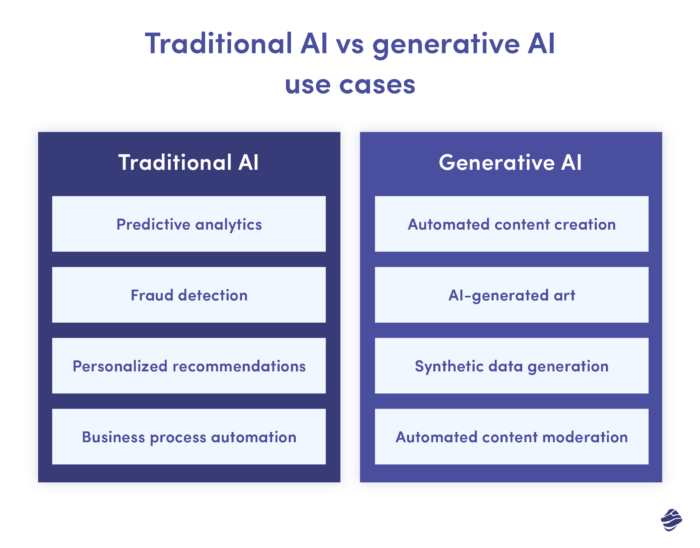
Traditional AI Use Cases
- Predictive Analytics: AI is extensively used in industries like manufacturing and transportation for predictive analytics. It analyzes data from machinery to predict potential failures, facilitating proactive maintenance and minimizing downtime.
- Fraud Detection: In the finance sector, AI algorithms are pivotal in detecting fraud. By scrutinizing transaction patterns, these systems identify patterns indicative of fraud, thus enhancing security and protecting assets.
- Personalized Recommendations: AI is a game-changer in e-commerce and streaming services, offering personalized recommendations. It can be used to analyze user behavior data and craft tailored suggestions, enriching customer experience and engagement.
- Business Process Automation: AI is revolutionizing business processes through the automation of tasks like document processing and data entry, increasing efficiency and allowing human employees to focus on complex tasks.
Generative AI Use Cases
- Automated Content Creation: Generative AI tools are employed in media and advertising for automated content generation, from news to marketing copy, thereby streamlining content creation.
- AI-Generated Art: Generative AI excels in the realm of digital art and music. Learning from existing content, these tools can produce unique artworks and musical compositions, marking a new phase in creative AI.
- Synthetic Data Generation: A key role of Gen AI is in generating synthetic data for training machine learning models, especially valuable in scenarios where real-world data is limited or privacy-sensitive.
- Automated Content Moderation: Generative AI models are increasingly used for moderating content on social media and digital platforms, analyzing vast user-generated content to filter inappropriate or harmful material.
Incorporating traditional AI or advanced Generative AI across different sectors illustrates their transformative capabilities, from the Google Assistant in our daily lives to advanced analytics in industry. These technologies are redefining the boundaries of user interaction, creative expression, and business efficiency.
Impact of AI and Generative AI on Various Industries
The revolution brought about by Artificial Intelligence and Generative AI is fundamentally altering operations, strategies, and consumer interactions across various industries.
McKinsey’s research underscores these technologies as major economic drivers, potentially adding trillions to the global economy. Deloitte’s report shows that 42% of companies are experimenting with Gen AI, with 15% actively incorporating it into their strategies.
Another Salesforce’s survey reveals that 70% of Gen Z engages with Gen AI applications, indicating a generational shift in technology use. This widespread adoption across industries and demographics highlights the transformative power of Artificial intelligence.
Here’s how key sectors are being reshaped by AI and Generative AI, with notable examples of applications in each.
Banking and Finance
McKinsey anticipates a potential annual value addition of $200 billion to $340 billion in banking due to Gen AI. Examples include AI solutions like ZestFinance, which uses AI for credit underwriting, and Kasisto’s KAI, a conversational AI platform enhancing customer service in banking. Gen AI is transforming the sector with innovations like Upstart, a lending platform using AI to streamline loan processing and risk assessment.
Retail and Consumer Goods
In retail and consumer goods, the potential impact of Gen AI ranges from $400 billion to $660 billion annually. AI applications like Shopify’s AI-powered recommendation engine exemplify the growing trend of AI features in mobile apps, enhancing user engagement and personalization. Gen AI is further elevating this sector with tools like Persado, which uses AI to generate optimized marketing language, enhancing customer engagement and sales.
Media, Technology, and Entertainment
In media and technology, AI is integral for content creation and audience engagement, with examples like Adobe Sensei, an AI and machine learning platform that powers creative tools. Gen AI steps in with platforms like Runway ML, enabling creators to generate unique visual effects and artworks, thereby expanding creative possibilities.
Pharmaceuticals and Life Sciences
AI’s role in pharmaceuticals and life sciences is exemplified by platforms like Atomwise, which uses AI for drug discovery, and DeepMind’s AI solutions for protein folding problems. Generative AI accelerates these processes with applications like Insilico Medicine, specializing in AI-driven drug discovery and aging research.
Miquido’s Insight: Miquido believes in the transformative potential of Generative AI within the business realm. Focusing on Generative AI app development, Miquido positions itself at the forefront of this technological wave, offering innovative solutions that cater to the evolving needs of industries, thereby setting new benchmarks in digital innovation.
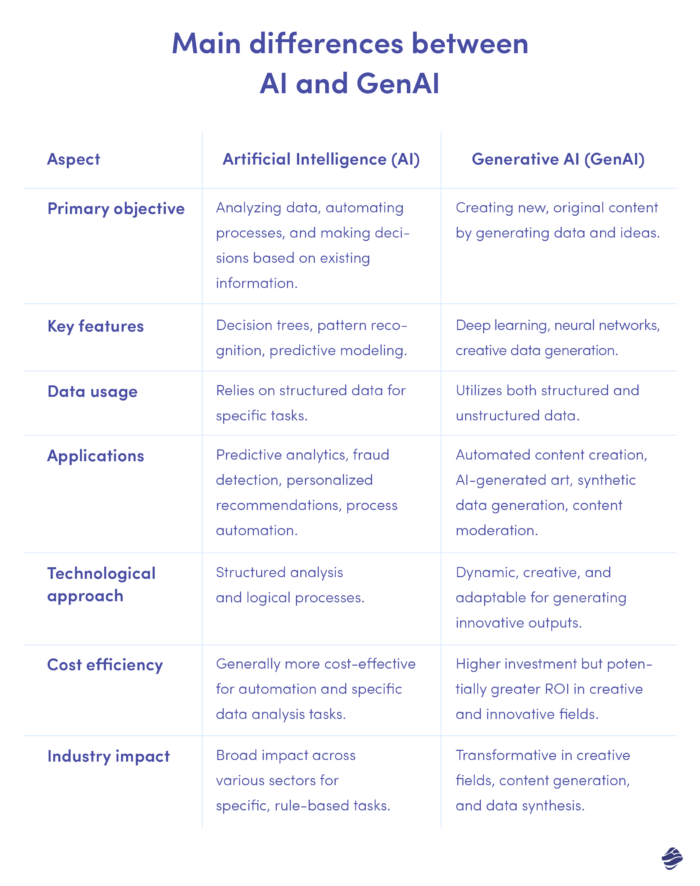
Generative AI vs AI: understanding the differences
In the ever-evolving landscape of technology, understanding the difference between AI and Gen AI is crucial. Here’s a quick comparison table that highlights their key differences:
Trends in AI and Gen AI
From the latest AI trends in mobile apps to the expansive capabilities of Generative AI, the evolving landscape of Artificial Intelligence is paving the way for innovative changes.
Generative Video and Multimodal Models
The leap from static images and texts to generative video is a milestone in Artificial Intelligence evolution. Tools like Deepfake technology and Adobe’s Project Aero, which allow for the creation of realistic video content top the list.
Multimodal models, such as OpenAI’s DALL-E, which can interpret and generate multi-format content, are also gaining prominence. This fusion of AI capabilities is not just enhancing user experience but is expected to revolutionize industries like advertising and entertainment, offering more immersive and interactive content.
Pro Tip: Businesses in creative industries should start exploring these tools to create engaging multimedia content, staying ahead in the competitive market.
The Generative Design Boom in Product Development
Generative design, particularly in CAD software like Autodesk Fusion 360, is transforming fields such as engineering and architecture. By inputting design goals and parameters, AI algorithms provide numerous innovative solutions, some of which may be unattainable through traditional methods. This not only cuts down development time but also opens up a realm of creative possibilities, potentially reducing material costs and environmental impact.
Pro Tip: Utilize generative design software to explore innovative solutions, potentially reducing costs and environmental impact.
Quantum AI and Web3
The intersection of Quantum Computing and AI, especially in the context of Web3, represents a futuristic synergy. Quantum AI, with its ability to process complex computations rapidly, could accelerate tasks like cryptographic processing and complex simulations. Web3’s decentralized nature, combined with Quantum AI, can enhance security and privacy in digital transactions and data management.
Pro Tip: Tech innovators Explore Quantum AI capabilities for high-security and speedy applications in the emerging Web3 landscape.
Large Language Models (LLMs)
GPT-3 and similar models are revolutionizing how we interact with AI. They are not just about text generation but also about understanding context and nuances in human language. This technology is finding applications in diverse fields, from creating educational content to assisting in legal document preparation.
Pro Tip: Businesses can leverage these models to automate content creation, customer service, and even coding, enhancing efficiency and innovation.
Autonomous Agents
The development of autonomous agents promises a new era of AI applications. These AI agents, capable of making decisions and learning independently, are set to transform sectors like transportation (autonomous vehicles), healthcare (robotic surgery assistants), and even personal assistance (advanced AI assistants).
Pro Tip: Invest in autonomous agent technology to enhance operational efficiency and offer cutting-edge services.
Open Models and Proprietary Models
The growing sophistication of open-source AI models is leveling the playing field. Tools like TensorFlow and PyTorch are making advanced AI technologies accessible to a broader audience, fostering innovation and creativity. This trend is also influencing cloud computing, with an increasing demand for cloud-based AI platforms and storage solutions to support these open-source models.
Pro Tip: Smaller companies and startups should consider leveraging open-source AI models to innovate and compete effectively in the market.
Ethical AI: Considerations Around AI and Gen AI
The ethical landscape surrounding Artificial Intelligence is complex and multifaceted, addressing issues ranging from fairness and bias to transparency and accountability. Here’s an overview of the key ethical considerations:
Transparency and Accountability
One of the foremost ethical considerations in AI and Gen AI is the need for transparency and accountability. As AI systems, especially Gen AI, become more complex and widely used, it becomes crucial to understand how these systems arrive at certain decisions or outputs.
The call for transparency is about making these processes clear to all stakeholders, ensuring that errors, biases, or potential misuses can be identified and addressed. The European Union’s AI Act, for example, mandates stronger transparency obligations for high-risk AI systems, including Gen AI, requiring public information on training data and model registration.
Bias and Fairness
Gen AI systems learn from large datasets, which often reflect existing societal biases. This can lead to AI models perpetuating or even amplifying these AI biases, resulting in unfair or discriminatory outcomes.
For instance, hiring algorithms might favor male candidates for technical positions due to historical data trends. Addressing these biases involves using diverse and representative datasets, identifying and correcting biased data points, and employing techniques like bias elimination and adversarial training.
Intellectual Property and Misinformation
Generative AI poses unique challenges in terms of intellectual property rights and the spread of misinformation. As these systems can generate new content, questions arise about the ownership of this content and the potential for creating misleading or false information. Developing ethical guidelines and legal frameworks to address these issues is critical to harness the positive potential of Gen AI while mitigating its risks.
Future Governance and Ethical Frameworks
As AI and Gen AI continue to evolve, so must the governance and ethical frameworks that guide their development and use. This involves not just regulatory compliance but also ethical decision-making within organizations developing or deploying these technologies. Collaborative efforts among governments, industry players, and academia are necessary to establish standards and practices that ensure the ethical and responsible use of AI and Gen AI.
How to Choose Between AI and Gen AI?
When it comes to integrating traditional AI or Generative AI into business operations or development projects, selecting the appropriate technology can be pivotal. Here’s a guide to help you make an informed decision:
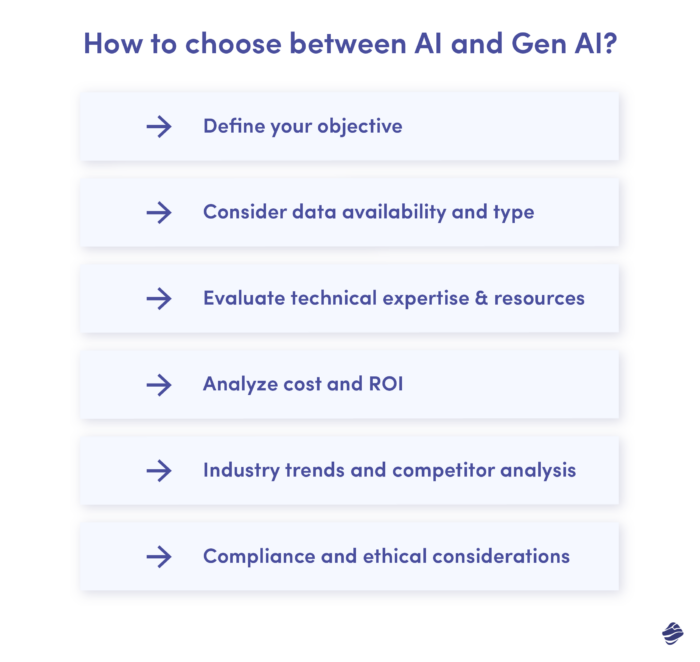
1. Define Your Objective
- For Traditional AI: If your goal involves tasks like analyzing data or automating processes for a particular job, traditional AI is suitable. It’s adept at handling well-defined rules and patterns, such as in predictive analytics.
- For Generative AI: Opt for Gen AI if your focus is on creating content or developing innovative solutions. Understanding Generative AI capabilities is key when your requirements include high creativity and adaptability, such as in digital art or advanced user interfaces.
2. Consider Data Availability and Type
- Data for Traditional AI: Traditional AI relies on structured data for specific tasks. If you have access to large, well-labeled datasets, AI can efficiently analyze data and generate outputs.
- Data for Generative AI: Generative AI relies on both structured and unstructured data, making it ideal for situations where you need to create content or derive insights from limited or sensitive data.
3. Evaluate Technical Expertise and Resources
- For Implementing Traditional AI: Deploying AI solutions typically requires understanding machine learning algorithms and data preprocessing.
- For Utilizing Generative AI: Implementing Gen AI might need more advanced skills in deep learning and neural networks, considering the complexity of models like GANs and VAEs.
4. Analyze Cost and ROI
Traditional AI might be more cost-effective for straightforward automation and data analysis tasks. In contrast, Generative AI could provide higher ROI in creative fields or when developing innovative products and services.
5. Industry Trends and Competitor Analysis
Stay updated with how competitors and industry leaders are using these technologies. This can provide insights into which technology might be more beneficial for your sector.
6. Compliance and Ethical Considerations
Ensure that your choice adheres to industry standards and ethical guidelines, focusing on data privacy, bias, and transparency.
In navigating the dynamic fields of traditional AI and Generative AI, leveraging their potential for your business is crucial. Miquido’s experienced AI Development team stand ready to help you leverage these technological advancements. With their expertise, Miquido can tailor AI solutions to meet your unique business challenges, ensuring you stay ahead in this fast-evolving digital landscape.
Unleash Innovation with Miquido’s AI Expertise
As we wrap up this exploration of AI and Gen AI, it’s clear that these technologies are not just futuristic concepts but transformative tools already reshaping our world. From the intricacies of their algorithms to their diverse applications across industries, they are truly redefining what’s possible.
Key Takeaways:
- One of the key differences between AI and Gen AI is that traditional AI excels in analyzing and automating, while Gen AI pioneers in creative content generation.
- Both AI and Gen AI are key players in industry transformations, from healthcare to finance.
- Choosing the right AI technology hinges on specific goals, data types, and creative needs.
- The evolving landscape of AI and Gen AI is rich with potential for future innovations.
Miquido stands at the forefront of this technological evolution, ready to guide and support businesses in navigating the complex but exciting world of AI and GenAI. With their expertise, Miquido isn’t just a service provider; they’re a partner in innovation, helping you harness these powerful technologies to meet your unique challenges and seize new opportunities.