Healthcare professionals today are under pressure from every direction — staff shortages, aging populations with complex needs, tighter regulations, and more data than any team can reasonably handle. At the same time, the demand for care that’s faster, more accurate, and more equitable keeps growing.
AI in the healthcare industry is starting to ease that load.
The healthcare AI market is expanding fast — growing more than 36% annually through 2030. That kind of momentum isn’t just hype. It marks a real turning point: AI is moving from an experimental tool to a core part of healthcare’s infrastructure.
How is AI Used in Healthcare
What makes generative AI different from older healthcare tools isn’t just that it’s smarter - it’s that it can work with language. Most previous systems were designed for narrow jobs: scan analysis, risk prediction, flagging anomalies. Useful, but specific. Generative AI, on the other hand, can generate images, videos, and text. It works with large amounts of data. It can summarize a patient’s history, draft clinical notes, answer medical questions, or create discharge instructions. In a field where so much depends on words - how doctors document, how patients are informed - that’s a big shift.
And it’s happening fast. In the U.S., about 85% of healthcare leaders say they’re either exploring or already implementing generative AI. Among those furthest along, most say they’re seeing real-world benefits: lower admin costs, better patient outcomes, fewer bottlenecks.
So how is AI used in healthcare now? That’s what the next sections unpack. Not blue-sky speculation - just examples of how generative AI is already embedded in care delivery, and what it’s likely to change next.
The acceleration curve
It’s no longer a question of if organizations will adopt AI in the healthcare industry - it’s how fast and at what scale. The healthcare sector is rapidly evolving as AI technologies are adopted to improve diagnostic accuracy, operational efficiency, and patient outcomes.
As of late 2024, 85% of healthcare leaders in the U.S. - across payers, providers, and tech groups - say they’re either exploring or actively deploying generative AI. Most are past the brainstorming stage. More organizations are now in implementation than in proof-of-concept, which is a quiet but telling sign: generative AI is starting to become infrastructure. Healthcare organizations are playing a critical role in evaluating, adopting, and integrating AI solutions to enhance clinical workflows and patient care.
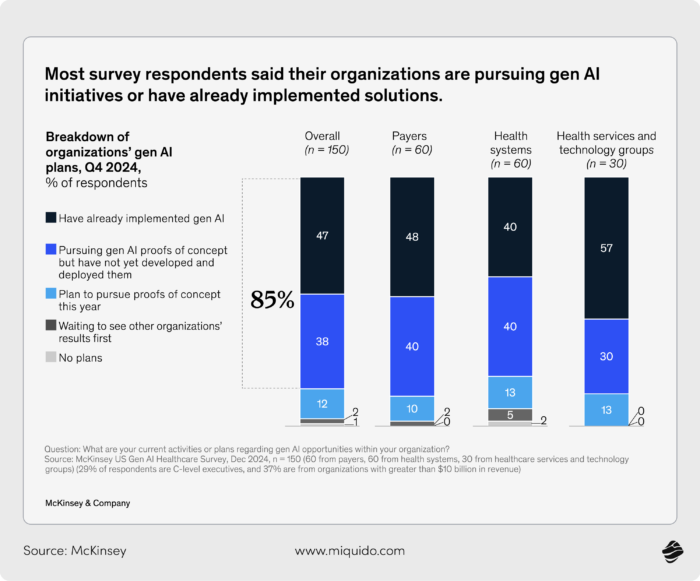
Among those who’ve already launched use cases, 64% report they’re seeing, or expecting, positive returns on investment. And that’s not from moonshot projects - it’s coming from areas like administrative automation, clinical documentation, scheduling, and patient communication. It’s the practical stuff that, until recently, drained time and energy from staff across the system. By leveraging AI, healthcare systems are able to achieve improved patient outcomes, greater efficiency, and better resource allocation.
The majority of adopters of AI in the healthcare industry aren’t doing this alone. About 60% are turning to third-party partners - often existing IT providers or large-scale cloud players - to help customize and integrate these tools. Only a fifth are trying to build capabilities fully in-house. That shift toward partnerships says something about pace: moving fast means collaborating, not reinventing. Organizations leverage AI to streamline healthcare delivery, automate labor-intensive tasks, and improve both operational workflows and patient experiences.
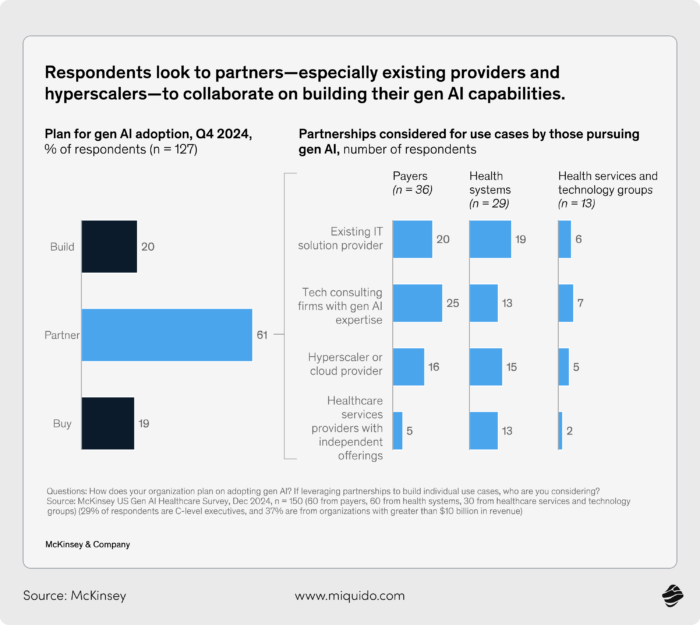
In short, adoption of AI in the healthcare industry is accelerating. What was once experimental is edging toward default. New models of healthcare delivery are emerging, as AI helps transform models of healthcare to address challenges like workforce shortages, rising costs, and the need for scalable, high-quality care. And as more healthcare systems build momentum - especially those with early success stories - laggards may find themselves playing catch-up in a field that’s quickly reshaping itself around new tools and new expectations.
How is artificial intelligence in healthcare used: real-world use cases
If the first chapter of AI in the healthcare industry was all about potential, the second is about proof. What used to live on whiteboards - smarter triage, faster diagnoses, personalized treatment - is now showing up in hospitals, clinics, and patient homes. Quietly, AI is starting to reshape how care actually works. AI is transforming the practice of medicine and medical practices by integrating advanced technologies into everyday healthcare delivery.
No, we don’t have autonomous AI doctors. But we do have tools that extend human judgment, reduce friction, and shift time back to the front lines - away from paperwork and toward patients. These AI-driven solutions are enhancing patient care, improving clinical outcomes, and supporting patient safety by reducing errors and optimizing treatment plans.
Here’s where it’s already happening, and where things are headed next.
1. Connected, augmented care
In the short term (0–5 years), AI in the healthcare industry is beginning to extend care beyond the four walls of the clinic. Augmented healthcare and connected care are becoming central to this transformation, enabling more intelligent and personalized approaches to treatment. Tools like symptom checkers, virtual assistants, and intelligent telehealth platforms are bridging the gap between patients and providers - particularly in primary care and mental health, where access and capacity remain ongoing challenges.
As the landscape evolves, ai augmented healthcare systems and the broader ai augmented healthcare system are being integrated to enhance clinical workflows, improve health equity, and enable more predictive and personalized care.
AI is also transforming medicine through ai augmented approaches, supporting precision medicine and data-driven disease management for better long-term outcomes.
What’s already in play:
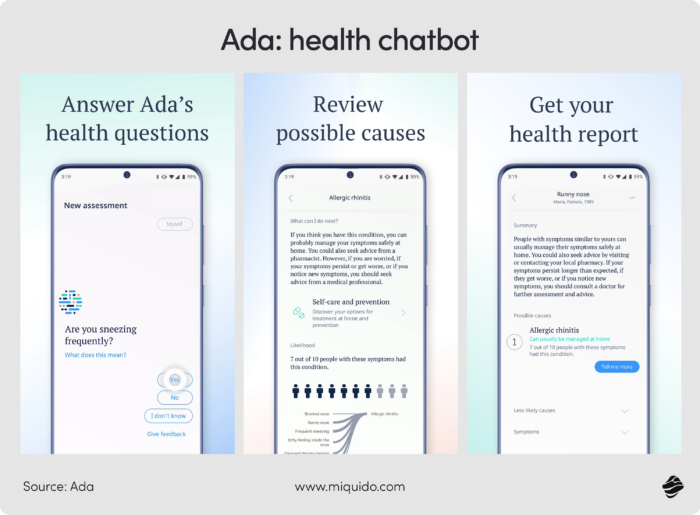
- Chatbots like Ada help users assess symptoms, navigate care options, and make informed decisions - all from their phones. Paired with wearables, they also surface trends in sleep, fitness, and overall wellness. These tools help automate high volume repetitive tasks and consuming high volume repetitive processes, reducing manual workload for providers.
- Ambient AI platforms such as Suki integrate directly into the exam room. They listen, transcribe, and generate clinical documentation in real time - allowing providers to focus on patients instead of keyboards.
- Remote monitoring tools like Emerald track respiration, sleep, and movement without wearables. Using contactless sensors and machine learning, they exemplify ambient intelligence: ever-present, passive, and always-on.
AI is also improving patient flow in healthcare settings by streamlining processes, reducing wait times, and optimizing resource allocation.
The rise of the patient support assistant
One of the clearest signs of AI’s real-world value in healthcare is the growing use of virtual patient assistants. These systems act as always-on front desks, handling routine questions through websites, apps, and voice interfaces without delays or escalation.
The benefits are immediate. AI assistants reduce call volumes, streamline workflows, and free up staff to focus on clinical priorities. Patients, in turn, get faster, clearer answers - whether they’re asking about fasting before a test or confirming appointment details.
What makes this shift significant is scale. Studies suggest that up to 80% of patient questions can now be handled end-to-end by generative AI - no human follow-up required. That includes everything from appointment reminders to post-visit instructions.
Crucially, these tools don’t just lighten the load. They improve access. Patients get support 24/7, in plain language, through the channels they already use. For many, this is their first meaningful interaction with a health system - and AI in the healthcare industry is helping set the tone.
As Bogusław Podhalicz, a UX expert at Miquido, points out, the shift to mobile AI transforms the patient relationship from reactive to proactive: "If we only have a web platform, the user visits ad hoc. But once we convince a user to download the app, we are with them for good... The system reaches out to you. It doesn’t wait — if it sees that test results have arrived and something is wrong, your phone vibrates in your pocket."
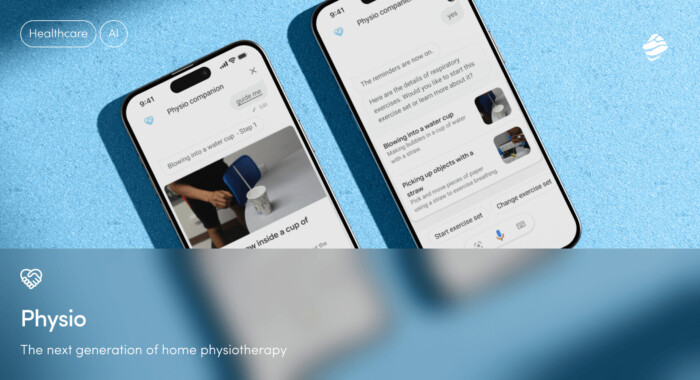
Case Study: Physio - voice-guided rehabilitation assistant
Developed with Centro Clinico Nemo and Google, Physio is a voice-enabled rehabilitation assistant designed for patients with neuromuscular disorders - many of whom face significant mobility and communication challenges.
The premise was simple: remove all friction. No apps, no logins, no screens. Just a voice interface, powered by Google Assistant, guiding patients through personalized rehab exercises. The assistant was developed using a human centred AI approach, focusing on user needs, stakeholder input, and real-world clinical workflows to ensure effective integration and adoption.
What makes Physio effective isn’t just the technology - it’s the delivery. The assistant adapts to each patient’s progress, providing continuity between sessions and supporting care at home. For clinicians, it offers a scalable way to extend therapy beyond the clinic. For patients, it’s intuitive, accessible, and easy to use - without compromising quality or consistency. Importantly, the system is designed to augment human intelligence, supporting clinicians and patients rather than replacing their expertise and judgment.
2. Precision therapeutics
AI’s superpower in the healthcare industry is pattern recognition - spotting signals in data that humans might miss. Deep learning and deep learning algorithms are now widely used in medical imaging and disease diagnosis, enabling more accurate and efficient analysis of complex medical data. In diagnostics, that means faster, more accurate detection. In therapeutics, it opens the door to treatments designed not just for “most people,” but for the individual.
AI is also transforming the early detection and management of chronic diseases, helping healthcare providers intervene sooner and improve patient outcomes.
Real-world examples include the use of deep learning algorithm models to analyze medical images for disease diagnosis, AI-driven tools developed by the pathology imaging co operative for pathology imaging, and advanced systems supporting prostate cancer and breast cancer detection and personalized treatment. AI applications also extend to diabetic retinopathy and radiotherapy planning, improving precision and patient care.
Pattern recognition at scale
Among all AI in the healthcare industry applications, diagnostics, particularly imaging, has advanced the fastest. AI isn’t just assisting radiologists anymore; in key areas, it’s matching or outperforming them. AI algorithms and AI systems are increasingly being used to analyze health records, enabling improved diagnostics, faster data retrieval, and more personalized patient care.
How is AI used in healthcare? Real-world examples:
- Diabetic Retinopathy Screening: Tools like LumineticsCore, approved by the FDA, can detect more-than-mild diabetic retinopathy with over 85% sensitivity and specificity. No human specialist required.
- Radiology and Pathology: AI systems are now interpreting chest X-rays, mammograms, skin lesions, and biopsy slides at expert level. In some cases, they’ve surpassed human performance, especially in pattern-heavy, high-volume tasks.

Looking ahead (5–10 years):
As AI in the healthcare industry becomes more integrated into clinical workflows, we’ll see broader adoption in under-resourced settings - bringing high-precision diagnostics to places with limited specialist availability.
From generic to tailored treatment
AI is beginning to rewire how we think about treating disease - not by following averages, but by learning from biological variation.
Emerging trends:
- Immunomics and synthetic biology: AI is now used to analyze massive multimodal datasets: genetic, clinical, behavioral, to identify which patients respond to which treatments. This is especially promising for oncology, neurology, and rare disease.
- Drug discovery: Platforms like DeepMind’s AlphaFold are reshaping early-stage drug development, predicting protein structures with high accuracy and speeding up discovery pipelines.
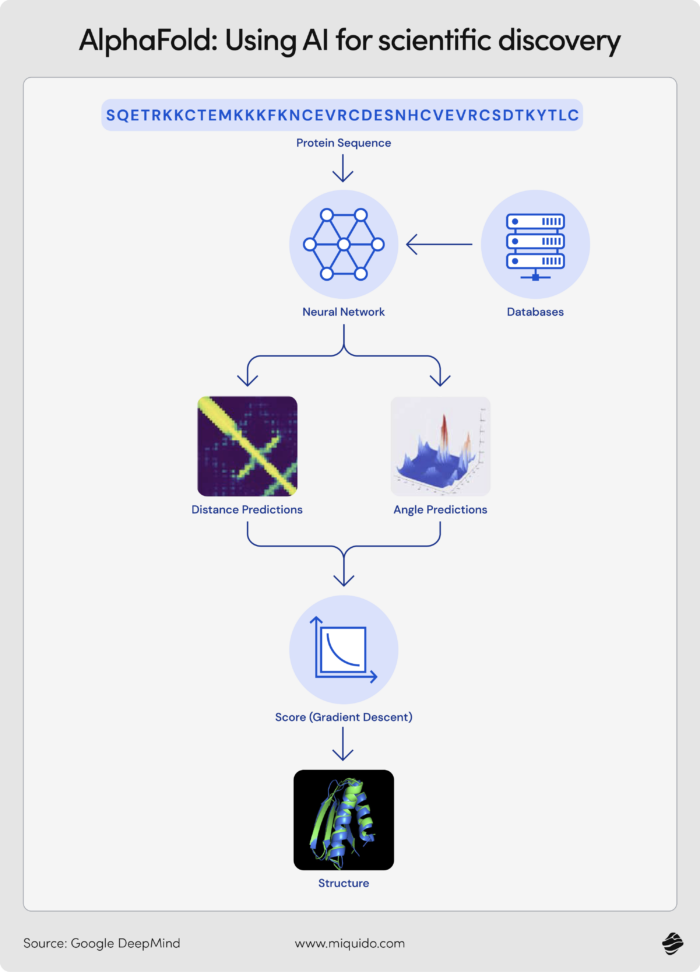
Medium-to-long term (5–10+ years):
As models become more data-efficient and less reliant on manual labeling, we’ll see AI co-develop new therapies alongside clinicians and researchers, with real-world feedback loops baked in.
3. AI-augmented, data-driven care with electronic health records
The long-term vision for AI in the healthcare industry goes well beyond diagnostics and documentation. The effective use of healthcare data and integration within health systems are crucial for enabling advanced AI applications that improve patient outcomes and operational efficiency. It’s about building systems that anticipate rather than react - shifting care from episodic to continuous, and from one-size-fits-all to precision-by-default.
What’s on the horizon:
- Digital twins: Virtual replicas of patients that simulate how an individual might respond to different treatments. The application of AI in creating digital twins and holomics is transforming how clinicians can test scenarios digitally before trying them in real life - reducing trial and error, and improving safety.
- Holomics: The integration of genomics, radiomics, proteomics, and clinical data to create an all-encompassing diagnostic profile. Instead of relying on isolated test results, providers get a layered, multi-dimensional view of patient health.
- Fully networked systems: Over the next decade, we’ll likely see hospitals, clinics, and even in-home devices tied together by AI-powered platforms that detect deterioration early, coordinate care automatically, and support proactive interventions across settings.
As these innovations progress, the direction of AI augmented healthcare systems will shape the future of medicine, driving more personalized, efficient, and data-driven care.
4. Medical intake assistants
Generative AI in the healthcare industry is also transforming one of the most overlooked parts of care delivery: the intake process.
The idea is simple: replace stacks of forms and rushed verbal checklists with an AI assistant that collects, structures, and summarizes key patient data - before the visit even starts. These AI assistants integrate with electronic health records, using natural language processing (NLP) to extract and process patient information efficiently.
How it works?
Patients interact with a secure chatbot or voice assistant - through an app, portal, or message link. It gathers symptoms, medication history, allergies, prior diagnoses, even insurance info. The assistant guides users through the process with natural language and prompts, then feeds the structured data directly into the provider’s system.
Take a patient visiting for chronic pain. Before they arrive, the intake assistant has already collected relevant history, flagged possible red flags, and noted medications. The doctor walks in with the context already in front of them. Instead of spending the first 10 minutes fact-finding, they can begin with diagnosis and care.
Across systems, this approach cuts down on redundant paperwork, shortens check-in times, and reduces documentation errors. It also ensures clinicians are working with cleaner, more reliable data - right from the start.
5. Learning assistants
Healthcare evolves fast. Guidelines change. Systems update. New staff arrive constantly. But traditional training methods - manual onboarding, long slide decks, static e-learning modules - aren’t designed to keep pace.
Generative AI is changing that. As a learning assistant, an AI agent can act as an on-demand coach that adapts to individual roles, specialties, and knowledge gaps. It’s always current. Always available. And always aligned to real clinical needs.
Learning that adapts to real learners
Unlike static e-learning modules, AI can tailor content to a user’s role, experience level, and even learning style. AI tools in medical education are specifically designed to address stakeholder needs, ensuring that both learners and educators benefit from adaptive, relevant content in a clinical context. A junior clinician might get walk-throughs of foundational procedures. A veteran provider can ask questions about protocol changes or emerging guidelines—and get immediate, evidence-based answers.
This isn’t theory. At Harvard Medical School, students are already engaging with AI tools from day one. Incoming students on the Health Sciences and Technology (HST) track now take a required course on AI in healthcare - one of the first such programs in the country. Meanwhile, the new AI in Medicine (AIM) PhD program has drawn hundreds of applicants for just a handful of spots, reflecting the field’s surging relevance.
These students aren’t just learning about AI. They’re using it - through “tutorbots” trained on HMS curricula, generative feedback tools for clinical skills training, and even course planning assistants that co-create learner-centered syllabi. This hands-on experience prepares them for the integration of AI in clinical practice and helps them understand the importance of applying AI within a clinical context.
“Tomorrow’s most successful physicians and researchers will be the ones who can harness generative AI for innovation and strategy,” said Taralyn Tan, assistant dean for educational scholarship at HMS.
Real tools, real impact for healthcare professionals
With AI-powered grading systems, HMS faculty now analyze short-answer responses at scale - identifying student strengths and weak points without spending hours on manual review. Clinical skills modules use LLMs to act as both standardized patients and feedback providers, enabling students to rehearse diagnosis and communication skills anytime, from anywhere.
This kind of just-in-time learning doesn’t just improve convenience. It improves performance. It makes training more accessible. And it helps future physicians develop the kind of critical thinking that complements - rather than competes with - AI. However, it is important to consider the ethical implications of using AI in medical training and assessment, particularly regarding patient safety, privacy, and fairness.
How is AI used in healthcare for scaling smarter training
Generative AI tools like AIDIFY, which we helped develop for a global pharmaceutical client, have shown similar impact. It matches users with personalized training modules with over 96% accuracy, while improving content engagement and retention by more than 40%.
The future of AI in the healthcare industry
Healthcare is entering a new era—one defined by smarter systems, earlier interventions, and more personalized care. AI is no longer on the sidelines; it’s becoming foundational to how care is delivered, managed, and experienced.
Looking ahead, we expect to see rapid progress across a few core areas:
- Predictive, proactive care powered by AI models that anticipate risk before symptoms appear
- More equitable access through virtual assistants, remote diagnostics, and language-aware tools
- Precision medicine at scale, driven by multimodal data and tailored treatment pathways
- Smarter workflows where clinicians are supported - not replaced - by AI systems.
Empower your healthcare journey with Miquido’s AI expertise
At Miquido, we see the convergence of AI and healthcare not as a tech story, but as a human one. Our vision is centered on building tools that reduce friction, save time, and give both patients and clinicians what they need - when they need it.
We work closely with healthcare providers to design AI solutions that are secure, intuitive, and deeply integrated into clinical practice. From early pilots to production-ready platforms, our goal is simple: create technology that feels less like software and more like support.
Whether you’re exploring your first AI pilot or scaling up an existing solution, Miquido brings deep expertise in both technology and healthcare. We’ll help you navigate the complexity - so you can focus on delivering better care.
Let’s turn potential into practice. Talk to us about your AI journey.

![[header] how ai is used in healthcare](https://www.miquido.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/06/header-how-ai-is-used-in-healthcare.jpg)



